Formula E
 | |
| Category | Single-seater |
|---|---|
| Country | International |
| Inaugural season | 2014–15 |
| Drivers | 22 |
| Teams | 11 |
| Chassis suppliers | Spark |
| Tyre suppliers | Hankook |
| Drivers' champion | |
| Teams' champion | |
| Official website | fiaformulae.com |

Formula E, officially the ABB FIA Formula E World Championship, is an open-wheel single-seater motorsport championship for electric cars. The racing series is the highest class of competition for electrically powered single-seater racing cars. The inaugural championship race was held in Beijing in September 2014.[1] Since 2020, the series has had FIA world championship status.[2]
The ABB FIA Formula E World Championship season consists of a series of races, each known as an e-Prix.[3] These take place in multiple countries and continents around the world, mostly on street circuits created specifically for Formula E on closed public roads in the centre of major cities, with a small number on purpose-built circuits such as Autódromo Hermanos Rodríguez in Mexico City.[4] A points system is used at each e-Prix to determine two annual World Championships: one for the drivers, and one for the constructors (the teams).[5] Each driver must hold a valid e-Licence issued by the FIA to compete.[6]
Formula E cars are the fastest regulated electric road-course racing cars in the world.[7] Major changes made for the 2022–23 season in the development of the Gen3 car were delivered as software updates directly to the advanced operating system built into the car.[8] The estimated top speed is 322 km/h (200 mph). The battery is also designed to be able to handle "flash-charging" at rates of up to 600 kW, allowing pitstop recharging into the championship for the first time. The wheelbase has been reduced from 3100 mm to 2970 mm and the weight reduced to 760 kg.[9]
Formula E shareholders include Liberty Global and Warner Bros. Discovery.[10] As of 2024, Formula E’s founder and Spanish businessman Alejandro Agag is the company’s Chairman, and the Chief Executive Officer is Jeff Dodds.[11]
History
[edit]The proposal for a city-based, single-seater electric car motor racing championship was conceived by Jean Todt, the president of the world governing body of motorsport, the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA), and presented to politicians Alejandro Agag and Antonio Tajani at a dinner at a small Italian restaurant in the French capital Paris on 3 March 2011.[12][13][14] Tajani was concentrated on the electrification of the automobile industry, reducing carbon-dioxide emissions and introducing hybrid and electric systems. Agag supported Todt's proposal after the latter discussed the FIA opening up a tender to organise the series. Agag told Todt that he would take on the task because of his prior experience in negotiating contracts with television stations, sponsorship and marketing.[15]
Since the 2020–21 season, Formula E is an FIA World Championship, making it the first single-seater racing series outside of Formula One to be given world championship status.[16]
Regulations
[edit]
The Formula E championship is currently contested by 22 drivers, and 11 teams as of the 2024 season.[17] The sport features electric-powered race cars similar in style to the hybrid-drive cars of Formula One. Racing generally takes place on temporary city-centre street circuits, that are around 1.9 to 3.4 km (1.2 to 2.1 mi) long, although the series is slowly moving towards racing on more traditional circuits, such as Portland International Raceway, and the Misano Circuit.[18][circular reference]
Practice
[edit]All practice sessions in Formula E are 30 minutes long, with the first practice session generally taking place on Friday afternoon, while the second takes place on Saturday morning (both sessions are held on Saturday morning in Monaco). During these sessions, the drivers are free to use the full qualifying power output (currently 350 kW (475 bhp)).[19] An additional practice session takes place on Sunday morning in "doubleheader" weekends, where the series runs two races on the same track on back to back days.
Qualifying
[edit]The qualifying session typically takes place later in the day and lasts approximately one hour. Under the current format (introduced in season 8), the drivers are split into two groups based on their position in the championship; those in odd-numbered places go into group A, while those in even-numbered places go into group B. The exception is in the first race of the season, where each team can nominate one driver into each group. Each group gets a 10-minute session to set a fastest lap at 300 kW, of which the top 4 of each group will advance to the "duels" stage, where drivers face off head-to-head at 350 W over a quarter-final, semi-final and final. The winner of the final then lines up in position 1, the loser of the final in position 2, the losers of the semi-final in positions 3 and 4, and the losers of the quarter-final in positions 5 through 8, in order of time set in their respective sessions. The rest of the drivers from the group stage are placed alternately from position 9, with the polesitter's group in the odd places, and the other group in the even places.[20][21]
Race format
[edit]Formula E, like most other major motorsport series, currently has races that have a certain lap distance set. Also, for every four laps that are spent under full course yellow or the safety car, an additional lap of racing is added to the race length.
A feature called 'Attack Charge' is expected to be introduced no earlier than Season 11, where the drivers will come into the pits to service a mandatory 30 second pit stop that will charge the batteries, and add 4kWh of energy to them, which will also unlock two enhanced Attack Mode boosts. In the race, the maximum power output of the cars is currently restricted to 300 kW (402 bhp).
Since the all-weather tyres are designed to last for a whole race, pit stops are only needed to change a punctured tyre or perform repairs on the car.
History of race formats
[edit]From Season 1–4, Formula E had a lap distance set, with pit-stops to swap cars halfway through as the batteries lacked the capacity to last the whole race. However, from Season 5, the race was set to 45 minutes plus one lap, as the introduction of the Gen2 car that year meant that pit stops were no longer necessary, as the battery now lasted for the full race, before the introduction of the Gen3 Car in Season 9, where Formula E reverted to the lap format.
For season 6 and 7,[22] for each minute spent under safety car or FCY, 1 kW⋅h of energy was removed from the total usable energy, giving drivers and teams more energy management tactics. In Season 8, a newly introduced 'added time' format was used, where every full minute under a safety car or full course yellow within the first 40 minutes, 45 seconds was added to the race time up to a maximum of 10 minutes, before the 'added lap' format that is currently used replaced the 'added time' format in Season 9.
Track formats
[edit]Formula E started out in 2014–15 as holding races solely on street circuits, many of them built as temporary circuits (e.g. Tempelhof Airport Street Circuit). The first race on a dedicated racetrack was held at Autódromo Hermanos Rodríguez in Mexico in the 2016–17 season, albeit in a heavily shortened track setup compared to the one used in Formula 1's Mexican Grand Prix.[23]
In the 2020–21 season, the Puebla ePrix and Valencia ePrix were held on configurations comparable to their full-length configurations, being 381 m (by skipping the International Road Course' leftmost corners)[24] and 629 m (by skipping turns 9 through 12 of the Grand Prix Circuit)[25] shorter respectively.
The first-ever Formula E race held on a full-length racetrack configuration of a circuit designed for other racing leagues, or in fact a longer one than the main configuration, was the 2023 Portland ePrix at the Portland International Raceway.[26]
In the 2019–20 season, Tempelhof hosted the first race held on a reverse configuration of a track's main layout in Formula E (previous examples in other racing leagues included IndyCar's Museum Park in Miami in 1995, and Circuit Zandvoort in the 1958 Tulip Rally).[citation needed]
Point scoring
[edit]Points are awarded to the top ten drivers using the standard FIA system (25–18–15–12–10–8–6–4–2–1). The driver securing the pole position is also awarded 3 points, while the driver setting the fastest lap (if they finish in the top ten) additionally receives 1 point (2 points during the first two seasons). In addition, for season six and seven (2019–21) the driver achieving the fastest lap during group qualifying was awarded 1 point.[27] The championship consists of both a drivers' and teams' championship. A driver's end of season total is made up of a driver's best results. A team's total is made up by counting both drivers' scores throughout the season.[21]
Fanboost
[edit]For Formula E's first eight seasons (2014–22), fans could vote for their favorite driver via the official website or app to potentially provide teams with an extra power boost which can be activated by pushing an overtake button. Voting started three days before the event and closed after the opening 15 minutes of the race. The five drivers that got the most votes each received an extra power burst that could be used in a 5-second window during the second half of the race.[21] Since the 2023 season, Fanboost was discontinued.[28]
Attack Mode
[edit]
With the fifth season, a feature called Attack Mode was introduced, in which drivers received an additional 25 kW in season 5 (35 kW in season 6 and 7)[29] of power after driving through a designated area of the circuit off the racing line. The duration of the boost mode and the number of boosts available are decided only shortly before each race by the FIA to reduce the time the teams have to find the optimal strategy.[30] All attack modes must be activated at the end of the race, but do not need to be used up (i.e. if a final attack mode is activated in the penultimate lap, the driver is not penalized for having it still activated at the end of the race). If there is a full course yellow period or a safety car, attack mode is not allowed to be activated.
The Attack Mode format was changed up for Season 9, as instead of a constantly changing number of times the drivers had to drive through the activation zone during the race, and also the changing amount of time that each Attack Mode period lasted, the drivers would now get a combined 4 minutes of Attack Mode to use, that would be used in 2 activation periods throughout the race. During the first activation period, drivers would have to choose their Attack Mode activation time 'strategy', where they could either pick from having 2 2-minute attack mode periods, a 1-minute to start and then a 3-minute period, or vice versa. From the 2023 Jakarta E-Prix, it was lengthened to a combined 8 minutes that could be deployed in 2 minutes and then 6 minutes or vice versa or 2 4-minute periods.
Attack Charge
[edit]In Season 9, a new feature known as Attack Charge was set to be introduced in a few races later in the season, however, due to the need to solve issues with the Gen3 car's new batteries, the production of the fast chargers were delayed, and as a result, after criticisms from the teams about shifting to a new race format midway through the season, the debut of Attack Charge was pushed back, and was not ready as of the end of Season 10. In Attack Charge races, the teams will be required to do a mandatory 30-second stop to recharge the car's batteries, and the stop will unlock two enhanced attack mode boosts, while also giving the drivers an extra 4 kWh of power to use throughout the rest of the race.[31]
Cars
[edit]Spark-Renault SRT_01E ("Gen1 Car")
[edit]
For the first four seasons, an electric racing car built by Spark Racing Technology, called the Spark-Renault SRT 01E, was used. The chassis was designed by Dallara, a battery system was created by Williams Advanced Engineering and a Hewland five-speed gearbox was used. Michelin was the official tyre supplier.[32][33][34] For the first season, 42 electric cars were ordered by the series. 4 cars were made available to each of the 10 teams and 2 cars were kept for testing purposes.[35]
This first Formula E car had a power of at least 190 kilowatts (250 hp). The car was able to accelerate from 0 to 100 km/h (0 to 62 mph) in 3 seconds, with a maximum speed of 225 km/h (140 mph).[36] The generators used to re-charge the batteries are powered by glycerine, a by-product of bio-diesel production.[37]
In the first season, all teams used an electric motor developed by McLaren (the same as that used in its P1 supercar). But since the second season, powertrain manufacturers could build their own electric motor, inverter, gearbox and cooling system although the chassis and battery stayed the same. There were nine manufacturers creating powertrains for the 2016–17 season: ABT Schaeffler, Andretti Technologies, DS-Virgin, Jaguar, Mahindra, NextEV TCR, Penske, Renault, and Venturi.[38]
Spark SRT05e ("Gen2 car")
[edit]
The second-generation ("Gen2") Formula E car was introduced in the 2018–19 season and featured significant technological advances over the previous Spark-Renault SRT 01E car – its 54 kWh battery and power output rising from 200 kW to 250 kW and top speed rising to around 280 km/h (174 mph). The arrival of the Gen2 car also saw an end to the series’ mid-race car-swaps.[39] They were equipped with Brembo braking systems, chosen by Spark Racing Technology as the sole supplier.[40][41] The cars were also equipped with the halo, a T-shaped safety cage designed to protect the driver's head in crashes and by deflecting flying objects.[42] Michelin remained as tyre manufacturer, supplying all-weather treaded tyres.[43]
Gen3 car (from 2023)
[edit]
The Gen3 Formula E car was unveiled to the public at the 2022 Monaco ePrix, for use in the ninth Formula E season (2022–23) onwards. Power levels for the car are 350 kW in qualifying and 300 kW in the race, while regeneration is allowed on both front (250 kW) and rear (350 kW) axles for a maximum of 600 kW recovery under braking. Regenerative braking could provide 40% of the total energy used within a race.
The estimated top speed is 322 km/h (200 mph).[44] The battery is also designed to be able to handle "ultra-fast charging" at rates of up to 600 kW,[45] allowing pitstop recharging into the championship for the first time.[46] The wheelbase has been reduced from 3100 mm to 2970 mm and the weight reduced to 760 kg.
Spark Racing Technology builds the chassis and supplies the front axle MGU, Williams Advanced Engineering supplies the battery, and Hankook supplies all-weather tyres incorporating bio-material and sustainable rubber.[47]
Gen4 car (from 2026)
[edit]The development of the Gen4 era of Formula E is already underway, with the extensive GenEVO programme, the championship’s development car. The intention is to introduce the new Gen4 car into the championship from Season 13 (2026–27) for the Gen4 era.[48]
Teams and manufacturers are already expressing interest in the Gen4 era, with the idea that many of the current championship teams will sign for all four years. Jaguar Racing is advancing in the field of Gen4 cars with by setting up a specialised Mechatronics unit under the supervision of Muin Ahmad, who recently lead the development of twin battery system of Formula E Cars.[49]
Comparison
[edit]| Gen1 | Gen2 | Gen3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Season introduced | S1 (2014/2015) | S5 (2018–2019) | S9 (2022/2023) |
| Length | 5320 mm or 17.45ft | 5160 mm or 16.92ft | 5016.2 mm or 16.45ft |
| Height | 1050 mm or 3.44ft | 1050 mm or 3.44ft | 1023.4 mm or 3.35ft |
| Width | 1780 mm or 5.83ft | 1770 mm or 5.80ft | 1700 mm or 5.57ft |
| Wheelbase | 3100 mm or 10.17ft | 3100 mm or 10.17ft | 2970.5 mm or 9.74ft |
| Mass (incl. driver) | 920 kg (battery 450 kg) | 900 kg (battery 385 kg) | 840 kg |
| Maximum power | 200 kW | 250 kW | 350 kW |
| Battery Capacity | 28 kWh | 52 kWh | 38.5 kWh |
| Maximum regeneration | 100 kW | 250 kW | 600 kW |
| Top speed | 225 km/h | 280 km/h | 320 km/h |
| Powertrain | Rear | Rear | Front and rear |
| Tyre Supplier | Michelin | Michelin | Hankook |
| Pole Time at Berlin | 1:08.312 | 1:06.227 | 1:05.605 |
| Range | 50 km | 100 km | 94 km |
Safety Car
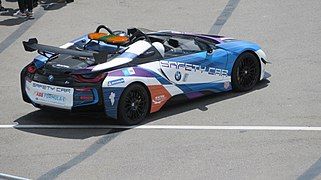
[edit]During the first seven seasons, a BMW i8 plug-in hybrid was employed as the Formula E safety car.[51] During the 2020–21 season, a Mini Electric (called the Electric Pacesetter by JCW) was used as safety car for selected races.[52] From 2022, a Porsche Taycan has been used.[53] Bruno Correia is the official safety car driver.
-
The BMW i8
Seasons
[edit]Champions
[edit]2014–15
[edit]
The calendar consisted of 11 races held in 10 different host cities: Beijing, Putrajaya, Punta del Este, Buenos Aires, Long Beach, Miami, Monte Carlo, Berlin, Moscow and finally London, where last two rounds of the championship took place.
The first Formula E race at the Beijing Olympic Green Circuit on 13 September 2014 was won by Lucas Di Grassi, after Nick Heidfeld and Nicolas Prost crashed out on the final corner. In the course of the season, there were 7 different race winners: Sébastien Buemi (three times), Sam Bird (twice), Nelson Piquet Jr. (twice), António Félix da Costa, Nicolas Prost, Jérôme d'Ambrosio and Lucas Di Grassi. The championship was decided with the last race in London, where Nelson Piquet Jr. became the first Formula E champion, only a single point ahead of Sébastien Buemi. Piquet, Buemi, and Di Grassi all had a theoretical chance at winning the title in the final round. The team championship was decided on the second to last race, with e.dams Renault (232 points) winning ahead of Dragon Racing (171 points) who surpassed ABT in the final round of the championship.
2015–16
[edit]The second season of Formula E started in October 2015 and ended in early July 2016. The calendar consisted of 10 races in 9 different cities. For this season eight manufacturers were introduced, who were allowed to develop new powertrains. Sébastien Buemi won the championship with only 2 points more than Lucas di Grassi by claiming the fastest lap in the final race in London.
2016–17
[edit]The 2016–17 FIA Formula E season was the third season of the FIA Formula E championship. It started in October 2016 in Hong Kong and ended in July 2017 in Montreal. Lucas di Grassi won the championship in the last race of the season, 24 points ahead of Sébastien Buemi and 54 points ahead of third-placed rookie driver Felix Rosenqvist. The Renault e.Dams team successfully defended their team championship title.
2017–18
[edit]The 2017–18 FIA Formula E season was the fourth season of the FIA Formula E championship. It started in December 2017 in Hong Kong and ended in July 2018. Jean-Éric Vergne clinched the title with a race to spare in New York by finishing fifth while title rival Sam Bird failed to score enough points to keep the fight going into the final race of the season.[54]
After a difficult first half of the season, Audi Sport ABT Schaeffler improved in the second half and passed Techeetah at the final race to claim the teams' championship by two points.[55]
2018–19
[edit]
The Gen2 race car was introduced for season five with significantly improved power and range, thus eliminating the need to change cars and pit stops altogether except for damage. However, cars are still vulnerable to power exhaustions if red flags and safety cars lengthen races. Gen2 also saw the introduction of the halo driver protection system.[56] The car was unveiled in January 2018.[57]

BMW, Nissan and DS Automobiles would join Formula E as official manufacturers for the 2018–19 season, with Nissan replacing Renault, which had exited the championship to focus its resources on its Formula 1 team.[58] The format of the races also changed from a set number of laps to 45 minutes plus one lap.[59]
The 2019 Hong Kong ePrix was the 50th race of Formula E since its inception in 2014. Formula E raced in 20 cities, across five continents, seen 13 global manufactures commit to the series. Four drivers have started all 50 Formula E races: Lucas di Grassi, Sam Bird, Daniel Abt and Jérôme d'Ambrosio.[60]
After the first race in New York City, Jean-Eric Vergne won his second Formula E championship, becoming the first driver to win more than 1 championship title, and a back-to-back championship title.[61] Techeetah won their first constructor's championship.[62]
2019–20
[edit]For the sixth season of Formula E, two more manufacturers joined the series: Mercedes-Benz and Porsche.[63][64] A number of rule changes were introduced to the championship, most notably the deduction of usable energy under safety car and Full Course Yellow conditions, with drivers having energy subtracted at 1kW⋅h per minute.[65] Due to the COVID-19 pandemic the championship was suspended in March 2020 and all scheduled races were eventually cancelled.[66] The season was completed in August with six races at the Tempelhof Airport Street Circuit in Berlin on three different layouts (a race on the reverse layout, a race on the normal layout, and a race with a new extended layout) with two races each.[67]
The season's champion was António Félix da Costa who clinched his first title with two races left. DS Techeetah became team champions for the second time in a row.[68]
2020–21
[edit]Starting with its seventh season, the Formula E Championship was granted FIA World Championship status, due to it having met the criteria of having four manufacturer competitors and races on three continents since the 2015–16 season.[69] The facelift of the Spark Gen2 car called the Gen2 EVO, was originally scheduled to debut in this season, but was later delayed and eventually cancelled due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[70]
In late 2020, Audi and BMW announced their withdrawal from Formula E after the 2020–21 season, although BMW and Audi allowed Andretti Autosport and Envision Racing respectively to continue using their powertrains during the 2021–22 season.[71]
The season ended in August 2021 with 15 races. Nyck de Vries claimed his first world champion title after winning two races, while Mercedes-EQ won the teams' championship.[72]
2021–22
[edit]The 2021–22 FIA Formula E season is the eighth season of the FIA Formula E World Championship and the final season of the "Gen2" car era.[73] The season started in January 2022 in Diriyah.
Instead of removing usable energy from drivers under the safety car and FCY, there will be added time to the race. For every full minute the race is neutralized within the first 40 minutes, there is 45 seconds of added time. This can add up to a maximum of 10 minutes.[74]
Race power was also increased to 220 kW and attack mode was increased to 250 kW, matching the power from Fanboost.
Season 8 also introduced a new qualifying format, featuring 2 groups, A and B, where the top 4 in each would progress to duels.[75] Stoffel Vandoorne won the Drivers title, whilst Mercedes EQ won the teams championship for the second time in a row.
2022–23
[edit]The 2022–23 FIA Formula E season was the ninth season of the FIA Formula E World Championship, and the debut season of the Gen3 era. It saw Maserati and McLaren make their debuts in the series and the return of Abt Sportsline with the Spanish brand Cupra Racing. Laps replaced timed races, and for every safety car or FCY intervention, there were added laps to compensate for missed racing laps.
Pit stops were originally also supposed to make a return to the series (in the form of Attack Charge) which was set to be trialed at select races, however the introduction of this race format was delayed to the 2023–24 season and beyond, after several issues with the new car's batteries came up before the season, which caused delays in the production of the fast chargers.
Originally also, in at least two races, each team would have to field a driver with no previous Formula E experience in the first practice session. However, after teams criticized this rule, the series then decided that instead as a compromise, they would hold two rookie test sessions, one being after the doubleheader Berlin E-Prix, and the other being before the doubleheader Rome E-Prix.
The drivers' championship was won by Jake Dennis (Avalanche Andretti Formula E), and the teams' championship was won by Envision Racing.
2023–24
[edit]The 2023–24 FIA Formula E was the tenth season of the FIA Formula E World Championship, with 16 races taking place from January to July 2024 across 10 venues. For the first time, it featured a championship for manufacturers (in addition to the existing drivers' and teams' championships).
The calendar Season 10 was announced in November 2023, featuring new venues Misano, Shanghai, and a world-first race held in the streets of Tokyo, Japan, with Portland expanding to a double-header.[76]
Attack Charge was scheduled to be introduced starting at the Misano E-Prix.[77] This new feature would have seen drivers take a mandatory pit stop in a specific window during the race, during which the car would have been recharged to award drivers two attack mode boosts and an extra 4 kWh (14.4 MJ) of energy throughout the rest of the race.[78] This feature was originally planned to be introduced in season 9, but after delays in production of the fast charging units it was postponed until season 10. This timeframe was then delayed once again, with the feature not introduced during season 10.[79]
The Drivers' Championship was won by Pascal Wehrlein (Porsche Formula E Team), the Teams' Championship was won by Jaguar Racing, and the Manufacturers' Trophy was won by Jaguar.
2024–25
[edit]The 2024–25 FIA Formula E is scheduled to be the eleventh season of the FIA Formula E World Championship, with 16 races set to take place from December 2024 to July 2025 across 10 venues. The races are set to be held across two calendar years for the first time since the 2019–20 season. Lola and Yamaha are set to join the series, and cooperate in developing their new powertrain, partnering ABT.
The calendar of Season 11 features new venues in Jeddah and Miami, and the return of the Jakarta ePrix, with Monaco and Tokyo expanding to double-headers.
Esport series
[edit]In 2019, the Virtually Live Ghost Racing app was launched. It allows fans to virtually drive alongside the real drivers as the race is going on.[80] In 2020, during the season suspension due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Formula E held an esport series called Race at Home Challenge.[81] In 2021, Formula E introduced a new series called Formula E: Accelerate using the online game rFactor 2. The first season of six races was held between January and March 2021. All Formula E teams participated in the series.[82][83] The series currently consists of professional sim racers racing virtually on selected race tracks from the season, with the events being called “majors”, before the finale on the London Circuit.
Support Series
[edit]FE School Series
[edit]During the first season, the FE School Series for student teams that developed their own electric car took place as support races at selected events.[84] The series was not continued during the second season.[85]
Roborace
[edit]Roborace was developing the world's first autonomous and electrically powered racing car.[86] The company planned to develop the first global championship for driverless cars.[87] It held demonstrations at selected races during the 2016–17 Formula E season and 2017–18 Formula E season.
Jaguar I-Pace eTrophy
[edit]Formula E and Jaguar ran a production-based support series with Jaguar I-Pace battery electric SUVs.[88] The series was called the I-Pace eTrophy and ran together with Formula E's fifth and sixth seasons (December 2018 to summer 2020). In May 2020, Jaguar announced the cancellation of the series, due to financial issues caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic.
NXT Gen Cup
[edit]In 2024 Formula E announced the NXT Gen Cup, founded in 2023, and the world's first 100% electric junior (ages 15–25) touring car series with both male and female drivers, would join as support series to the championship.[89] The NXT Gen Cup is set to feature at all four European rounds of season 10 in Misano, Monaco, Berlin and London.[90]
Media
[edit]Television
[edit]Formula E provides comprehensive live television coverage shown via major broadcasters around the globe (CBS Sports, The Roku Channel, TNT Sports UK, CCTV-5, Eurosport, J Sports, Ziggo Sport Totaal, TV Cultura).[91][circular reference] English language programming is produced by Whisper, while Aurora Media Worldwide produces the main worldwide broadcast.[92]
Presenters
[edit]Up until Season 9, the world feed was presented frequently by Jack Nicholls and Dario Franchitti, with Nicki Shields acting as pit lane reporter. However, just before the 2023 Jakarta E-Prix, Nicholls was fired after allegations of inappropriate behaviour towards women, and Ben Edwards, who had already done motorsport commentary for 3 decades, replaced him in the commentary booth from Jakarta E-Prix until the Portland E-Prix. Later that season, Tom Brooks, known as "the Voice of Gran Turismo" became the main commentator of Formula E from the Rome E-Prix onwards.
Former footballer Jermaine Jenas, ex-F1 and Formula E driver Karun Chandhok, 4-time Indycar Champion Dario Franchitti, and Nicki Shields will anchor Formula E's English Language Programming for Season 10.
Radzi Chinyanganya, and Saunders-Carmichael Brown will serve as pit lane reporters.
The expert lineup for Formula E includes ex-Formula E team boss and former driver Allan McNish, Andre Lotterer, rally driver Catie Munnings, and tenacious racing driver, Billy Monger, with former F1 veteran David Coulthard, and inaugural W Series Champion Jamie Chadwick making guest appearances throughout the season.[93]
Documentaries
[edit]Directors Fisher Stevens and Malcolm Venville created a documentary movie about the 2017–18 season called And We Go Green. It highlights some of the innovations and challenges of Formula E and follows several drivers and rivalries throughout the season. The film was co-produced by Leonardo DiCaprio and premiered at the 2019 Toronto International Film Festival.[94]
Formula E debuted its own documentary series, called 'Unplugged' on 22 November 2021, which was similar to Formula One's Netflix Drive to Survive series. The series gave a behind-the-scenes look on every driver’s journey through the 2020–21 season. Unplugged returned for a second season in March 2023, showcasing the 2021–22 season, and for a third season in January 2024 showcasing the 2022–23 season.[95]
Gallery
[edit]-
Track signage highlighting sustainability.
-
E-Village, 2015.
-
At the podium in 2017.
-
Alejandro Agag (far right) helped to create the championship series.
-
Berlin E-Prix 2023 pole position trophy.
-
View of the tail light illumination.
-
Safety car charging, 2023.
-
Paddock area, 2023.
-
Close-up of a Gen3 driver.
-
Team Mercedes-EQ pitbox.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Telegraph Sport (13 September 2014). "Formula E opens with spectacular crash involving Nick Heidfeld and Nicolas Prost as Lucas di Grassi claims win". Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ^ "Formula E gets world championship status for 2020/21 season". autosport.com. 3 December 2019. Archived from the original on 12 November 2021. Retrieved 25 June 2021.
- ^ "Rules and Regulations". fiaformulae.com. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ "Formula E World Championship: Mexican ePrix to kick off new 2024 campaign – 'A great place to start'". TNT Sports. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ "Rules and Regulations". fiaformulae.com. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ "2023–2024 FIA FORMULA E WORLD CHAMPIONSHIP SPORTING REGULATIONS" (PDF).
- ^ "New third-generation Formula E car is fastest ever electric racer". autocar.co.uk. Haymarket Automotive. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ "Formula E Gen3: What is it and what is new". autosport.com. Motorsport Network. 29 April 2022. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ "Formula E And FIA Reveal All-Electric Gen3 Race Car In Monaco". fiaformulae.com. 28 April 2022. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ Georg, Szalai (9 March 2015). "Discovery, Liberty Global Buy Stake in Formula E Racing Circuit". hollywoodreporter.com. Penske Media Corporation. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ Cian, Brittle (17 May 2023). "Formula E names Jeff Dodds as new CEO". blackbookmotorsport.com. SportsPro Media. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ Carp, Sam (2 February 2018). "Electrified: Alejandro Agag on Formula E's path to the podium". SportsPro. Archived from the original on 12 May 2018. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- ^ Sam, Mallinson (13 April 2017). "From Dream to Reality: Formula E was born in Paris". FIA Formula E Championship. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- ^ Chowdhury, Saj (10 September 2014). "Formula E: Does it have a future in a world dominated by F1?". BBC Sport. Archived from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- ^ Kingham, Ben (13 May 2016). "On the subject of Power". Current E. pp. 40–59. Archived from the original on 15 July 2019. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- ^ "Formula E to be given world championship status for 2020–21". BBC. 3 December 2019. Archived from the original on 23 November 2020. Retrieved 3 December 2019.
- ^ "Teams & Drivers". FIA Formula E. Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 10 April 2022.
- ^ "List of Formula E ePrix's and Circuits". Wikipedia.
- ^ "Formula E Rules and Regulations". www.fiaformulae.com. Formula E. 6 March 2018. Archived from the original on 25 March 2023. Retrieved 14 April 2023.
- ^ Smith, Sam (15 October 2021). "Full details of new Formula E qualifying format revealed". The Race. Archived from the original on 5 July 2022. Retrieved 5 June 2022.
- ^ a b c "Rules and Regulations". fiaformulae.com. 25 November 2021. Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 23 April 2022.
- ^ "Formula E changes rules to encourage energy management". www.motorsport.com. 14 June 2019. Archived from the original on 17 July 2019. Retrieved 10 April 2022.
- ^ "Formula E heads for history-making race in Mexico City". CNN. 10 March 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- ^ "AN IN-DEPTH LOOK INTO THE UPCOMING PUEBLA E-PRIX". e-racing. 28 May 2022. Retrieved 17 January 2023.
- ^ "Valencia E-Prix circuit layout confirmed". Just Electric. 19 April 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- ^ "Formula E goes full Indycar! – PORTLAND e-Prix". Autosport.com. 21 June 2023. Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- ^ "New FE points rule to make qualifying "all the more important"". www.motorsport.com. Motorsport.com. 18 November 2019. Archived from the original on 18 May 2021. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
- ^ Smith, Sam (17 October 2022). "Formula E to drop Fanboost from 2023 season". The Race. Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ "Rules and Regulations". FIA Formula E. Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ Herrero, Daniel (8 June 2018). "Formula E confirms details of unique boost mode". Speedcafe.com. Archived from the original on 16 April 2021. Retrieved 12 August 2018.
- ^ "Sporting regulations announced for Season 9". FIA Formula E. Archived from the original on 20 November 2022. Retrieved 20 November 2022.
- ^ "Michelin confirmed as official tyre supplier for FIA Formula E Championship". Formula E Operations. FIA Formula E Championship. 28 March 2013. Archived from the original on 5 April 2013.
- ^ "Renault signs with Spark Racing Technology and Formula E Holdings as Technical Partner in the FIA Formula E Championship" (PDF). Formula E Operations. FIA Formula E Championship. 15 May 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 June 2013.
- ^ "Williams partners with Spark Racing Technology to provide battery expertise for the FIA Formula E Championship". WilliamsF1.com. Williams F1. 11 June 2013. Archived from the original on 16 October 2014.
- ^ "Formula E buys 42 electric racers for 2014 circuit". green.Autoblog.com. 18 November 2012. Archived from the original on 24 July 2014. Retrieved 1 August 2014.
- ^ "Guide to – Car – Specifications". Archived from the original on 30 November 2015. Retrieved 24 November 2015.
- ^ "Formula E power generation". Archived from the original on 12 February 2015.
- ^ "FE–Ten teams entered for the third Formula E season". 1 July 2016. Archived from the original on 18 April 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ^ "Formula E presents Gen2 car for 2018/19 season". www.motorsport.com. Motorsport.com. 6 March 2018. Archived from the original on 18 September 2020. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- ^ "The New Tech Headache Formula E Teams Must Solve". InsideEvs. 21 October 2018. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- ^ "Next generation Formula E Car breaks cover in Geneva". FiaFormulaE. 6 March 2018. Archived from the original on 12 November 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- ^ Stewart, Jack (24 February 2018). "Formula 1's New 'Halos' Could Save Drivers' Heads—And Give Engineers Headaches". Wired. Archived from the original on 3 March 2021. Retrieved 21 March 2019 – via www.wired.com.
- ^ Alex Kalinauckas. "Formula E unveils its Gen2 car for 2018/19 season". Autosport. Archived from the original on 9 May 2019. Retrieved 9 May 2019.
- ^ "Formula E and FIA reveal all-electric Gen3 race car in Monaco". FIA Formula E. 28 April 2022. Archived from the original on 15 July 2022. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ^ "FORMULA E AND FIA REVEAL ALL-ELECTRIC GEN3 RACE CAR IN MONACO". fiaformulae.com/. FormulaE. 29 April 2022. Archived from the original on 14 August 2022. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ^ "Formula E's Gen3 Regeneration Concept Agreed". the-race.com. the-race. 18 June 2020. Archived from the original on 5 December 2021. Retrieved 1 July 2020.
- ^ "The FIA and Formula E Build Ever More Relevant Future". www.fia.com. FIA. 1 July 2020. Archived from the original on 30 November 2021. Retrieved 1 July 2020.
- ^ Dominik, Wilde (9 December 2023). "Formula E confirms Gen4 suppliers". racer.com. Racer Media & Marketing, Inc. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ Sam, Smith (4 May 2022). "WHAT WENT ON AT FORMULA E'S SECRET GEN4 BRAINSTORM MEETING". The Race. The Race Media Ltd. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ "Formula E Gen3: What is it and what is new". www.autosport.com. 29 April 2022. Archived from the original on 3 December 2022. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ^ "The BMW i8: From vision to icon, from bestseller to classic of the future" (Press release). Munich: BMW Group. 11 March 2020. Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ "MINI Electric Pacesetter to become Official FIA Formula E Safety Car". fiaformulae.com. 29 March 2021. Archived from the original on 11 April 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2021.
- ^ "Porsche Taycan revealed as new Formula E Safety Car". FIA Formula E. 18 January 2022. Archived from the original on 18 January 2022. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
- ^ Grzelak, Antonia (14 July 2018). "Vergne crowned champion at Audi festival in New York". www.e-racing.net. Archived from the original on 7 November 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- ^ Grzelak, Antonia (15 July 2018). "Audi grabs the last title as Formula E's first chapter ends". www.e-racing.net. Archived from the original on 11 April 2021. Retrieved 15 July 2018.
- ^ Laurence Edmondson. "Formula E reveals next generation car with Halo". ESPN. Archived from the original on 16 December 2021. Retrieved 7 February 2019.
- ^ "Formula E unveils new 'Gen 2' car for Season 5". Crash. 30 January 2018. Archived from the original on 16 December 2021. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- ^ "FIA confirms 11-team Formula E entry list for Season 5". crash.net. 28 August 2018. Archived from the original on 24 December 2018. Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- ^ Alex Kalinauckas. "Formula E's 'Mario Kart' plan formalised for 2018/19 season by FIA". Autosport. Archived from the original on 28 November 2020. Retrieved 7 February 2019.
- ^ "Stat Attack: 10 things you didn't know about the race in Hong Kong". Formula E. 7 March 2019. Archived from the original on 26 September 2020. Retrieved 9 March 2019.
- ^ Jerry Perez. "Jean-Eric Vergne Clinches Formula E World Championship in New York City". The Drive. Archived from the original on 8 May 2021. Retrieved 18 October 2019.
- ^ "Da Costa joins championship-winning team DS Techeetah". Formula E. Archived from the original on 30 October 2020. Retrieved 18 October 2019.
- ^ "Mercedes-Benz to enter Formula E in Season 6 – Formula E". fiaformulae.com. 24 July 2017. Archived from the original on 19 August 2021. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ^ "Porsche set to compete in Formula E from Season 6 – Formula E". fiaformulae.com. 28 July 2017. Archived from the original on 11 April 2021. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ^ Soulsby, Chris. "Formula E: Formula E confirms 2019/20 season rule and regulation changes". Motorsport Week. Archived from the original on 3 December 2019. Retrieved 3 December 2019.
- ^ "Formula E and FIA take decision to temporarily suspend season". fiaformulae.com. 13 March 2020. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ "FIA Formula E Returns to Racing with Six Races in a row in Berlin". fia.com. 17 June 2020. Archived from the original on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- ^ "Da Costa crowned ABB FIA Formula E Champion and DS Techeetah seals Teams' title as Vergne wins Round 9". fiaformulae.com,date=2020-08-09. Archived from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 20 August 2020.
- ^ "Formula E receives FIA world championship status for 2020/21". www.motorsport.com. 3 December 2019. Archived from the original on 25 May 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2019.
- ^ "FE delays Gen2 Evo car as part of new cost saving measures". www.autosport.com. 9 April 2020. Archived from the original on 18 September 2020. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ^ Gitlin, Jonathan M. (3 December 2020). "Audi and BMW to both leave Formula E—here's why that's OK". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on 26 August 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ^ "De Vries and Mercedes claim Formula E world titles". the-race.com. 15 August 2021. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ "Formula E's Gen 2 EVO car Cancelled". Formula E Zone. 19 August 2020. Archived from the original on 20 March 2021. Retrieved 29 January 2022.
- ^ "What new 'extra time' rule will do to Formula E". The Race. 19 October 2021. Archived from the original on 10 April 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2022.
- ^ "DIRIYAH PREVIEW: Everything you need to know ahead of the Season 8 opener". FIA Formula E. 25 January 2022. Archived from the original on 18 May 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2022.
- ^ "Formula E Announces Biggest Calendar Yet For Season 10". fiaformulae.com. 22 November 2023. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ Golding, Nick (8 January 2024). "Dennis, Cassidy and Evans on 'risky' Misano Attack Charge introduction plan". motorsportweek. Archived from the original on 9 January 2024. Retrieved 6 July 2024.
- ^ Grangier, Dorian (31 December 2023). "The "Attack Charge" is coming in 2024: how does it work?". autohebdof1.com. Archived from the original on 9 January 2024. Retrieved 6 July 2024.
- ^ "Latest delay for Formula E pitstop format explained". The Race. 17 April 2024. Retrieved 6 July 2024.
- ^ "Race against the grid in real-time as Virtually Live Ghost Racing launches". FIA Formula E. 26 April 2019. Archived from the original on 17 January 2022. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
- ^ Smith, Sam (15 April 2020). "Formula E online series launched with elimination race format". The Race. Archived from the original on 5 March 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- ^ "Formula E: Accelerate esports competition sparks search for next-gen electric racing stars". FIA Formula E. 7 January 2021. Archived from the original on 3 April 2022. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
- ^ Kew, Matt (7 January 2021). "Formula E launches new Accelerate Esports competition". www.autosport.com. Archived from the original on 14 April 2022. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
- ^ "Formula E's School Series begins in Buenos Aires". fiaformulae.com. 19 December 2014. Archived from the original on 25 July 2015. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
- ^ "Exclusive: schools series axed". current-e.com. 5 October 2015. Archived from the original on 16 December 2015. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
- ^ "Formula E & Kinetik announce driverless support series". fiaformulae.com. 27 November 2015. Archived from the original on 2 February 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
- ^ "Formula E is planning the first racing series for driverless cars". engadget.com. 28 November 2015. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.
- ^ "FFormula E and Jaguar to launch support series". fiaformulae.com. 12 September 2017. Archived from the original on 12 September 2017. Retrieved 12 September 2017.
- ^ "Formula E Announces NXT Gen Cup As Support Series For Next Generation Of Drivers". fiaformulae.com. 8 February 2024. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ Dixon, Ed (12 February 2024). "Formula E launches NXT Gen Cup support series". blackbookmotorsport.com. SportsPro Media. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- ^ "List of Formula E broadcasters". Wikipedia.
- ^ "FORMULA E APPOINTS WHISPER FOR NEW-LOOK AND EXPANDED BROADCAST COVERAGE". whisper.tv. November 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ "Formula E Lead Presenters For Season 10". Formula E. 6 December 2023. Retrieved 6 December 2023.
- ^ "'And We Go Green' Review: Start Your (Quiet) Engines". The New York Times. 4 June 2020. Archived from the original on 14 September 2020. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
- ^ "Go Behind-The-Scenes Of Season 9 With Formula E: Unplugged". Formula E. 19 December 2023.