English: Images
March 11, 2015
http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/spaceimages/details.php?id=pia19058
http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=4507
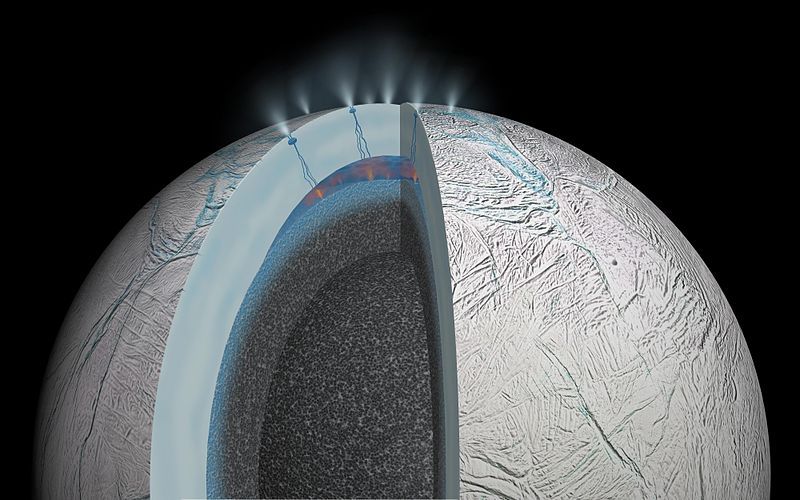
Enceladus: Possible Hydrothermal Activity (Artist's Concept)
This cutaway view of Saturn's moon Enceladus is an artist's rendering that depicts possible hydrothermal activity that may be taking place on and under the seafloor of the moon's subsurface ocean, based on recently published results from NASA's Cassini mission.
Hydrothermal activity is a process where seawater infiltrates and reacts with a rocky crust, emerging as a heated, mineral-laden solution. This is a natural occurrence in Earth's oceans.
Researchers think microscopic grains of rock detected in the Saturn system by Cassini most likely form when hot water containing dissolved minerals from the moon's rocky interior travels upward, coming into contact with cooler water. Temperatures required for the interactions that produce the tiny rock grains would be at least 194 degrees Fahrenheit (90 degrees Celsius).
On Earth, the most common way to form silica grains of the 6-to-9-nanometer size found by Cassini is hydrothermal activity involving a specific range of conditions. Namely, when slightly alkaline, slightly salty water that is super-saturated with silica undergoes a big drop in temperature.
Gravity science measurements from Cassini also suggest Enceladus' rocky core is quite porous, which would allow water from the ocean to percolate into the interior. This would provide a huge surface area where rock and water could interact.
Cassini first revealed active geology on Enceladus in 2005 with evidence of an icy spray issuing from the moon's south polar region and higher-than-expected temperatures in the icy surface there. With its powerful suite of complementary science instruments, the mission soon revealed a towering plume of water ice and vapor, salts and organic materials that issues from relatively warm fractures on the wrinkled surface. Gravity science results published in 2014 strongly suggested the presence of a 6-mile- (10-kilometer-) deep ocean beneath an ice shell about 19 to 25 miles (30 to 40 kilometers) thick.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit
http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and
http://www.nasa.gov/cassini.