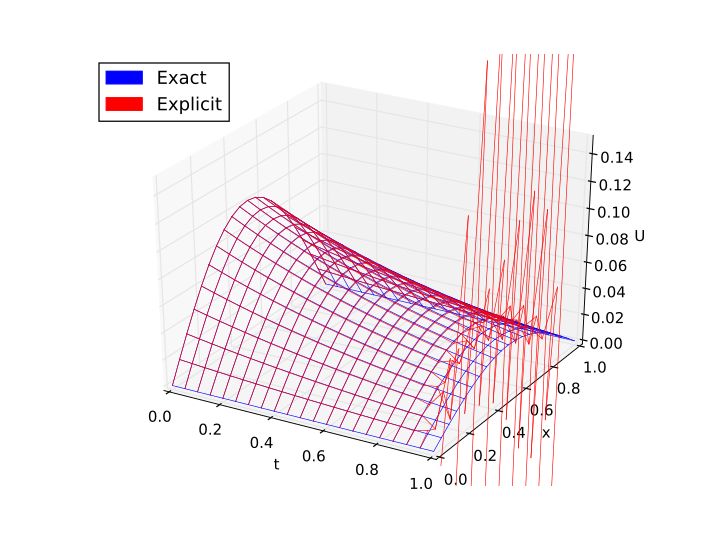
# Explicit method to solve the head equation.
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
t0 = 0.0
t_final = 1.0
n_grid = 20
dt = t_final / n_grid
dx = 1.0 / n_grid
T = np.arange(t0, t_final+dt, dt)
X = np.arange(0, 1+dx, dx)
ax = pl.figure().add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.set_xlabel('t')
ax.set_ylabel('x')
ax.set_zlabel('U')
ax.set_xlim([t0,t_final])
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
Umax= .15
ax.set_zlim([0, Umax])
# Exact solution
def exact(t, x):
return np.exp(-t)*np.sin(np.pi*x)/(np.pi*np.pi)
for t in T:
for x in X:
if t>t0:
ax.plot([t-dt, t],[x, x],[exact(t-dt, x), exact(t, x)], 'b-', linewidth=0.5)
if x>0.0:
ax.plot([t, t],[x-dx, x],[exact(t, x-dx), exact(t,x)], 'b-', linewidth=0.5)
# Explicit method
r = dx/(dt*dt)/(np.pi*np.pi)
U = [[0.0 for _ in X] for _ in T]
for i in range(len(T)):
for j in range(len(X)):
if i==0:
U[i][j] = exact(T[i], X[j])
elif j==0 or j==len(X)-1:
U[i][j] = 0
else:
U[i][j] = (1-2*r)*U[i-1][j] + r*U[i-1][j-1] + r*U[i-1][j+1]
for i in range(len(T)):
for j in range(len(X)):
if 0 < U[i][j]: # select the approximate values within the bound to display
if i>0:
ax.plot([T[i-1], T[i]],[X[j], X[j]],[U[i-1][j], U[i][j]], 'r-', linewidth=0.5)
if j>0:
ax.plot([T[i], T[i]],[X[j-1], X[j]],[U[i][j-1], U[i][j]], 'r-', linewidth=0.5)
bluePatch = mpatches.Patch(color='blue', label='Exact')
redPatch = mpatches.Patch(color='red', label='Explicit')
pl.legend(handles = [bluePatch, redPatch], loc=2)
pl.show()