File:Fibr.jpg
Appearance
Size of this preview: 800 × 440 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 176 pixels | 640 × 352 pixels | 916 × 504 pixels.
Original file (916 × 504 pixels, file size: 54 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
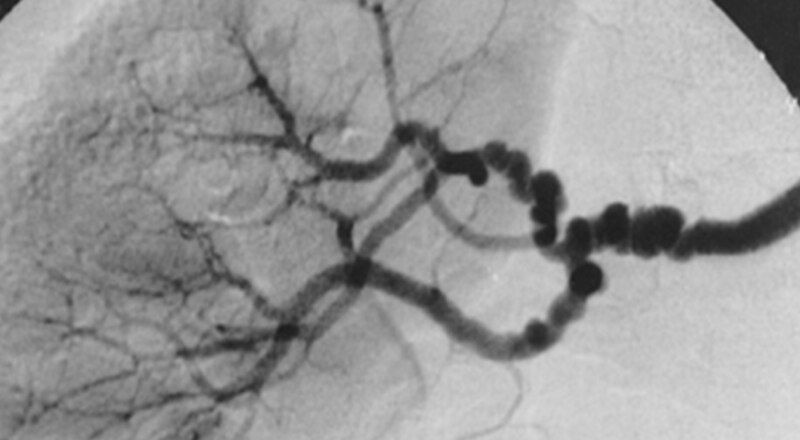
| current | 11:56, 21 August 2007 |  | 916 × 504 (54 KB) | Filip em | {{Information |Description=The "string-of-beads" feature in medial fibromuscular dysplasia. The sign is caused by areas of relative stenoses alternating with small aneurysms. The diameters of the aneurysms exceed the normal diameter of the artery. The sig |
File usage
The following page uses this file:
Global file usage
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on ar.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ca.wikipedia.org
- Usage on de.wikibooks.org
- Usage on es.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on id.wikipedia.org
- Usage on it.wikipedia.org
- Usage on la.wikibooks.org
- Usage on lv.wikipedia.org
- Usage on pl.wikipedia.org
- Usage on sr.wikipedia.org
