Elm leaf beetle
| Elm leaf beetle | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Coleoptera |
| Family: | Chrysomelidae |
| Genus: | Xanthogaleruca |
| Species: | X. luteola
|
| Binomial name | |
| Xanthogaleruca luteola (Müller, 1766)
| |
| Synonyms | |
Xanthogaleruca luteola, commonly known as the elm-leaf beetle, is a beetle species in the family Chrysomelidae that is native to Europe but invasive in other parts of the world.[2][3]
Description
[edit]
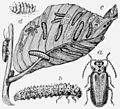
The imago (adult beetle) is 6–8 mm in length, and ranges from yellow to green in colour, with a spot on its head, an hourglass mark and two spots on the pronotum, and a broad, dark stripe along the edge of each elytron. The larvae are usually black, occasionally black and yellow, with multiple rows of dots on the back and on the sides and < 13 mm long. The pupae are orange-yellow with black chaetae. The ova are yellow, and laid in spindle-like clusters of < 25 on the undersides of the elm leaves.
Distribution
[edit]These beetles are common in the Western Palearctic realm from Portugal to Central Asia. Indigenous to Europe, they were accidentally introduced to North America and Australia, and are now widespread, and are serious pests in Australia[2] and parts of North America.[3]
Gallery
[edit]-
Drawing of beetle, larva, and eggs published in The New International Encyclopædia, v. 7, 1905
-
Larva of X. luteola on an elm leaf
-
Skeletonized leaves of parasitized elm
Ecology
[edit]X. luteola is a serious pest of the elm. Both the adults and larvae feed on the emergent leaves of the elm. Repeated heavy infestation rarely kills the tree outright, but weakens it, rendering it vulnerable to disease. Falling branches encourage elm bark beetles (Scolytus multistriatus and S. schevyrewi) to proliferate; the beetles are vectors of Dutch elm disease.[4]
Elm leaf beetles become active in the spring once temperatures rise above 52 °F (11 °C). In fact, weather is one of the most limiting factors in their population growth. A late spring freeze or long winter can kill off entire colonies.[4] The imagines depart their hibernation sites (often houses), the females laying their ova on the underside of the elm leaves. The ova hatch after one week, and the larvae immediately feed on the underside of the leaves. This larval stage lasts between two and three weeks, at the end of which larvae migrate to the lower part of the trees in search of bark crevices in which to pupate. The next generation emerges in midsummer after two to three weeks' pupation, and begins feeding on the leaves. The female can lay about 800 ova, but this ovipositing may be interrupted by shortening of the photoperiod to less than 14 hours, inducing a brief feeding bout before the search for a hibernation site.[5][6]
Hosts are known to include English elm (U. minor 'Atinia'), wych (Scots) elm (Ulmus glabra), American elm (Ulmus americana), Siberian elm (Ulmus pumila), and Chinese elm (Ulmus parvifolia), as well as complex hybrids such as 'Homestead'.[5] The beetle has also been reported on Zelkova serrata.[6]
When X. luteola oviposits, U. minor releases plant volatiles which recruit the egg parasitoid Oomyzus gallerucae. U. minor is able to distinguish between oviduct secretions (small molecule proteinaceous compounds) and damage which occurs in the natural course of oviposition, releases different volatiles upon detection of the oviduct compounds. O. gallerucae is then able to distinguish between these different sets of volatiles and is only attracted to oviposition. Gravid X. luteola females also respond, but inversely: They are attracted to volatiles indicating undamaged and/or unoviposited Ulmus material. Gene expression studies have shown a large number of genes to be involved in the oviposition response process.[7] (See Tritrophic interactions in plant defense.)
Jasmonic acid is released during gravid females' herbivory on Ulmus spp.[7]
Symptoms
[edit]The first and most apparent symptoms are of skeletonization. During feeding, elm leaf beetle larvae skeletonize the leaves. They leave the outer edge and veins of the leaf intact, which gives the foliage a net-like appearance. Areas around the feeding site dry up and die, causing the leaf to drop prematurely. Adults, on the other hand, chew small, irregularly shaped holes in the expanding leaves. Trees that lose their leaves often develop a second set, only to have them consumed when the next generation is produced.[8]
Controls
[edit]In North America, there are few natural enemies, but in Europe, the larva of the beetle are often heavily predated by the chalcidoid wasp Oomyzus gallerucae.[9][7] Insecticide sprays are of little use since by the time the infestation is apparent, the application will be too late to be effective. However, tree trunks banded with insecticides can limit repetition the following year by killing the larvae as they descend before hibernation. Soil injection[5] presents a non-invasive alternative to trunk injections with a 2-year effect on the X. luteola population.
Since overwintering elm leaf beetles infest the homes of those close to an elm leaf beetle infestation, it is suggested that all cracks outside the house should be sealed. It is discouraged to use insecticides unless there are really heavy colonies.[10]
Nearly all chemicals currently used commercially in Australia to treat Elm Leaf Beetle, regardless of brand name or delivery method, are neonicotinoid insecticides. This is the chemical type that has, from 2016 onward, a ban placed on it by the European Commission, owing to the association between the widespread use of these chemicals and their impact on bee populations.[11]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d "Xanthogaleruca luteola". ecoport.org. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ a b "Pyrrhalta luteola (elm leaf beetle)". Invasive Species Compendium. Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International.
- ^ a b http://cisr.ucr.edu/elm_leaf_beetle.html - Center for Invasive Species Research
- ^ a b "Elm Leaf Beetle Management". Statewide Integrated Pest Management Program. 2014.
- ^ a b c "Elm Leaf Beetle Management | Treatment for leaf damage".
- ^ a b Sinclair et al. 1987
- ^ a b c Hilker, Monika; Fatouros, Nina E. (2015-01-07). "Plant Responses to Insect Egg Deposition". Annual Review of Entomology. 60 (1). Annual Reviews: 493–515. doi:10.1146/annurev-ento-010814-020620. ISSN 0066-4170. PMID 25341089.
- ^ "Elm leaf beetle". The Morton Arboretum. Archived from the original on 2015-09-05. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ^ Meiners, T, and Hilker, M. (1997). Host location in Oomyzus gallerucae (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), an egg parasitoid of the elm leaf beetle Xanthogalereuca luteola (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Oecologia, Vol. 112, No. 1 / Sept. 1997, pp 87-93. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. ISSN 0029-8549 (print), 1432-1939 (online)
- ^ "Elf leaf beetles". Colorado State University. Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ^ Foote, Natasha (2021-05-06). "EU Court backs Commission's ban on controversial neonicotinoid pesticides". www.euractiv.com. Retrieved 2024-06-14.