Trans-Golgi network vesicle protein 23 A
| TVP23A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | TVP23A, FAM18A, YDR084C, trans-golgi network vesicle protein 23 homolog A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 3665441; HomoloGene: 19919; GeneCards: TVP23A; OMA:TVP23A - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Trans-Golgi network vesicle protein 23 A (TVP23A) is a protein coded for the TVP23A gene, formerly known as FAM18A.[5] TVP23A is located on chromosome 16.[6] It is known to have human paralogs, TVP23B and TVP23C, as well as orthologs in many different species, notably yeast, mice, and chickens.[7] The general consensus on the TVP23A protein indicate that it has some function in the late Golgi apparatus and is involved in retrograde transport from endosomes back into the Golgi apparatus. The nature of this transport is still unknown.[8]
Gene
[edit]Locus
[edit]TVP23A is located at cytogenic band 16p13.13, on the negative strand of Chromosome 16.[6]

Alternative Names
[edit]TVP23A stands for Trans-Golgi network Vesicle Protein 23A TVP23A, is the current name for the protein. Aliases of TVP23A include FAM18A, and rarely YDR084C.[5]
mRNA
[edit]Isoforms
[edit]There are two known isoforms of TVP23A, variant one and variant two, with variant one being the more common variant in humans.[6]
Protein
[edit]Structure
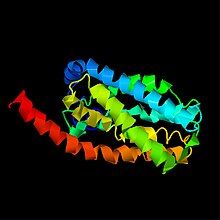
[edit]TVP23A is a member of the pfam superfamily containing the domain of unknown function 846 (DUF846).[9] TVP23A has a predicted molecular weight of 24.1 kilodaltons, an isoelectric point of 6.5, and relatively high amounts of tryptophan and phenylalanine.[10] The secondary structure of TVP23A consists primarily of alpha helices composing 4 transmembrane domains.[11] There is not much information on the tertiary structure of TVP23A or its homologs. iTASSER[12] was used to generate a prediction for the folding pattern of TVP23A, which supports the presence of multiple helix structures.
Expression
[edit]TVP23A is ubiquitously expressed in all human tissues.[13] There is evidence of higher expression in the brain tissue of mice.[14] The promoter for TVP23A is GXP_91266, spanning 1403 base pairs located on the negative strand of chromosome 16.[15]
Function
[edit]The hypothesized function of TVP23A is a transmembrane protein involved in retrograde transport of vesicles from early endosomes into the late Golgi apparatus.[16] TVP23A interactions with SNARE TVI1 were found to be required for retrograde transport. [17]
Interacting Proteins
[edit]TVP23A has been found to interact with four different proteins via Yeast two hybrid arrays.[18] Two of these proteins, YIPF1 and YIPF2, are believed to be Golgi transport proteins.
| Protein | Experiment | Function |
|---|---|---|
| SCAND1 | Two hybrid array | Potentially a transcription factor (SCAN domains common in ZFP) |
| WIPF2 | Two hybrid array | Believed to be involved in actin filament remodeling |
| YIPF1 | Two hybrid array | Golgi transport protein |
| YIPF2 | Two hybrid array | Golgi transport protein |
Homology
[edit]Homologous Domains
[edit]TVP23A is a DUF846 containing protein, which is homologous throughout TVP-type proteins. This domain contains the 4 transmembrane domains of TVP23A[19]
Paralogs
[edit]TVP23A has two paralogs, TVP23B and TVP23C. TVP23B and TVP23C are 96% similar to each other, and both are located on chromosome 17.[20] Due to the locations of these three genes, and their identities to each other, it is probable that ancestral TVP23 underwent duplication and translocation, giving rise to TVP23A on chromosome 16 and TVP23B/C on chromosome 17, which then underwent a second duplication to form TVP23B and TVP23C.
| Gene | Seq Length | Seq Identity | Chromosome |
|---|---|---|---|
| TVP23A | 213 | 100% | 16 |
| TVP23B | 205 | 54% | 17 |
| TVP23C | 203 | 53% | 17 |
Orthologs
[edit]TVP23A has been found in all multicellular eukaryotes, including fungi. This gene has not been found in bacteria.[21]
| Genus and species | Common Name | Order | Date of Divergence | NCBI Accession Number | Seq Length | Seq Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Human | Primate | 0 | NP_001072980 | 213 | 100% |
| Pan troglodytes | Chimp | Primate | 6.4 | XP_009428557.1 | 213 | 98% |
| Mus musculus | Mouse | Rodentia | 88 | NP_001013800.1 | 222 | 85% |
| Rattus norvegicus | Rat | Rodentia | 88 | NP_001101733.1 | 222 | 84% |
| Canis lupus familiaris | Dog | Carnivora | 94 | XP_547129.2 | 213 | 97% |
| Camelus ferus | Wild Bactian Camel | Ceratiodactyla | 94 | XP_006190640.1 | 213 | 92% |
| Bubalus bubalis | Water Buffalo | Ceratiodactyla | 94 | XP_006068214.1 | 213 | 93% |
| Miniopterus natalensis | Natal Long-fingered Bat | Chiroptera | 96 | XP_016053077.1 | 213 | 93% |
| Myotis brandtii | Brandt's Bat | Chiroptera | 96 | XP_005871809.1 | 213 | 93% |
| Condylura cristata | Star Nose Mole | Soricomorpha | 96 | XP_012587517.1 | 213 | 92% |
| Erinaceus Europaeus | European Hedgehog | Soricomorpha | 96 | XP_016047734.1 | 251 | 68% |
| Falco peregrinus | Peregrin Falcon | Aves | 312 | XP_005244242.1 | 204 | 64% |
| Gallus gallus | Chicken | Aves | 320 | XP_015150063.1 | 213 | 74% |
| Gekko japonicus | Schlegel's Japanese Gecko | Reptile | 320 | XP_015265390.1 | 210 | 75% |
| Thamnophis sirtalis | Garter Snake | Reptile | 320 | XP_013925075.1 | 308 | 30% |
| Rana catesbeiana | American Bullfrog | Amphibian | 352 | ACO51802.1 | 206 | 52% |
| Xenupus tropicalis | African Clawed Frog | Amphibian | 353 | XP_017953113.1 | 198 | 71% |
| Callorhinchus milii | Australian Ghostshark | Chimaeriformes | 465 | XP_007903081.1 | 206 | 70% |
| Rhizopus microsporus | Rhizopus | Fungi | 1105 | CEI91429.1 | 231 | 35% |
| Mortierella elongata | Mortierella | Fungi | 1105 | OAQ36303.1 | 218 | 35% |
| dictyostelium lacteum | Dictyostelium | Fungi | 1480 | KYQ94004.1 | 220 | 34% |
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000166676 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000050908 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "TVP23A".
- ^ a b c "GeneCards". GeneCards.
- ^ "AceView". AceView.
- ^ "GenAtlas". GenAtlas.
- ^ "DUF846".
- ^ "SAPS". Biology Workbench. SDSC.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "TMHMM". Biology Workbench.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "I-TASSER server for protein structure and function prediction". zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu.
- ^ "Gene: TVP23A". www.ensembl.org.
- ^ "GDS3142 / 1435130_at". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ "ElDorado". Genomatix.de. Archived from the original on 2001-02-24. Retrieved 2017-04-25.
- ^ Inadome, Hironori; Noda, Yoichi; Kamimura, Yurika; Adachi, Hiroyuki; Yoda, Koji (February 2007). "Tvp38, Tvp23, Tvp18 and Tvp15: Novel membrane proteins in the Tlg2-containing Golgi/endosome compartments of Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Experimental Cell Research. 313 (4): 688–697. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.11.008. PMID 17178117.
- ^ Stein, Ivar S.; Gottfried, Anna; Zimmermann, Jana; Fischer von Mollard, Gabriele (1 April 2009). "interacts genetically with the yeast SNARE and functions in retrograde transport from the early endosome to the late Golgi" (PDF). Biochemical Journal. 419 (1): 229–236. doi:10.1042/BJ20081973. PMID 19076069. S2CID 24826243.
- ^ "IntAct". www.ebi.ac.uk.
- ^ "Pfam: Family: DUF846 (PF05832)". pfam.xfam.org.
- ^ "BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool". blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ "UCSC Genome Browser Home". genome.ucsc.edu.




