Draft:TC-C 14G
| Submission declined on 5 December 2024 by Pygos (talk). This submission does not appear to be written in the formal tone expected of an encyclopedia article. Entries should be written from a neutral point of view, and should refer to a range of independent, reliable, published sources. Please rewrite your submission in a more encyclopedic format. Please make sure to avoid peacock terms that promote the subject.
Where to get help
How to improve a draft
You can also browse Wikipedia:Featured articles and Wikipedia:Good articles to find examples of Wikipedia's best writing on topics similar to your proposed article. Improving your odds of a speedy review To improve your odds of a faster review, tag your draft with relevant WikiProject tags using the button below. This will let reviewers know a new draft has been submitted in their area of interest. For instance, if you wrote about a female astronomer, you would want to add the Biography, Astronomy, and Women scientists tags. Editor resources
|  |
 Comment: This article is very difficult to understand as it is written right now. Please fix its prose to make it more understandable to laypeople (or at least, those only with basic knowledge of biomolecules). Also, the majority of citations are devoted to the Synthesis section. More citations should be about its biological activity. Pygos (talk) 03:43, 5 December 2024 (UTC)
Comment: This article is very difficult to understand as it is written right now. Please fix its prose to make it more understandable to laypeople (or at least, those only with basic knowledge of biomolecules). Also, the majority of citations are devoted to the Synthesis section. More citations should be about its biological activity. Pygos (talk) 03:43, 5 December 2024 (UTC)
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H17Cl2F2NO4 |
| Molar mass | 492.30 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
TC-C 14G is a potent, high affinity inverse agonist of the CB1 receptor: (EC50 = 11 nM in cAMP assay; Ki = 4 nM). Demonstrates high efficacy in a hypothermia assay (ID50 = 5 mg/kg) in vivo.[1]
Similar to rimonabant (and related agents such as giminabant), TC-C 14G potentially might have use in the treatment of obesity.
Synthesis
[edit]Literature report:[2] Patent (Ex 108):[3] Prec:[4]
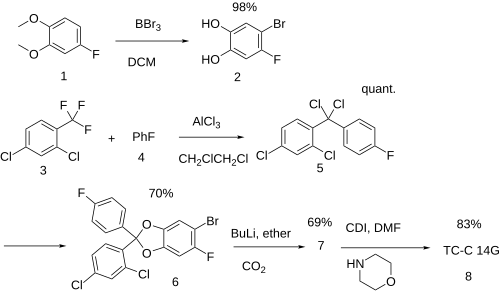
- 4-fluoroveratrole [398-62-9] (1)
- 4-bromo-5-fluoro-benzene-1,2-diol [656804-73-8] (2)
- 2,4-dichlorobenzotrifluoride [320-60-5] (3)
- Fluorobenzene [462-06-6] (4)
- 2,4-dichloro-4'-fluoro-diphenyldichloromethane [656803-77-9] (5)
- 5-bromo-2-(2,4-dichloro-phenyl)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-benzo[1,3]dioxole, PC22475200 (6)
- PC22475029 (7)
References
[edit]- ^ "tc-c-14g_4345". Trocris.
- ^ Alig L, Alsenz J, Andjelkovic M, Bendels S, Bénardeau A, Bleicher K, et al. (April 2008). "Benzodioxoles: novel cannabinoid-1 receptor inverse agonists for the treatment of obesity". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 51 (7): 2115–27. doi:10.1021/jm701487t. PMID 18335976.
- ^ WO 2004013120, Alanine A, Beleicher K, Guba W, Haap w, Kuber D, Luebbers T, Plancher JM, Rogers-Evans M, Schneider G, Zuegge J, Roche O, "Novel benzodioxoles", assigned to Hoffmann La Roche Inc.
- ^ Furlano DC, Kirk KL (October 1986). "An improved synthesis of 4-fluoroveratrole. Efficient route to 6-fluoroveratraldehyde and 6-fluoro-D, L-DOPA". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 51 (21): 4073–4075. doi:10.1021/jo00371a032.
