Draft:Dual Source Operation
Submission declined on 14 January 2025 by RangersRus (talk).
Where to get help
How to improve a draft
You can also browse Wikipedia:Featured articles and Wikipedia:Good articles to find examples of Wikipedia's best writing on topics similar to your proposed article. Improving your odds of a speedy review To improve your odds of a faster review, tag your draft with relevant WikiProject tags using the button below. This will let reviewers know a new draft has been submitted in their area of interest. For instance, if you wrote about a female astronomer, you would want to add the Biography, Astronomy, and Women scientists tags. Editor resources
|  |
| Submission declined on 11 January 2025 by Theroadislong (talk). This draft's references do not show that the subject qualifies for a Wikipedia article. In summary, the draft needs multiple published sources that are: Declined by Theroadislong 9 days ago.
|  |
| Submission declined on 3 January 2025 by DoubleGrazing (talk). This submission is not adequately supported by reliable sources. Reliable sources are required so that information can be verified. If you need help with referencing, please see Referencing for beginners and Citing sources. This submission appears to read more like an advertisement than an entry in an encyclopedia. Encyclopedia articles need to be written from a neutral point of view, and should refer to a range of independent, reliable, published sources, not just to materials produced by the creator of the subject being discussed. This is important so that the article can meet Wikipedia's verifiability policy and the notability of the subject can be established. If you still feel that this subject is worthy of inclusion in Wikipedia, please rewrite your submission to comply with these policies. Declined by DoubleGrazing 17 days ago. |  |
 Comment: If this original research is re-submitted I suggest it is rejected outright. Theroadislong (talk) 08:59, 13 January 2025 (UTC)
Comment: If this original research is re-submitted I suggest it is rejected outright. Theroadislong (talk) 08:59, 13 January 2025 (UTC)
 Comment: The TImes of India is not a reliable source and none of the sources mention dual source operation? Theroadislong (talk) 15:26, 12 January 2025 (UTC)
Comment: The TImes of India is not a reliable source and none of the sources mention dual source operation? Theroadislong (talk) 15:26, 12 January 2025 (UTC)
Dual Source Operation (DSO) means that most of all the electronic equipment today used in homes and industries can be operated directly with DC 230 volts HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) supply instead of 230 volts normal AC traditional supply without any hardware changes[1][2][3].Inverters are not necessary. The devices/equipment operated by the normal AC or DC supply (HVDC power feed) are Television, personal computer, fluorescent lamp with electronic ballast, CFL lights, led lights, mobile chargers, digital set top boxes, DVD players, electronic table and ceiling fans, motor with VFC control[1][2][3]. List may go up.
The concept is based on the basic principle of current flow through the diodes used in the bridge rectifier[4] present in the second stage of AC to DC Switched Mode Power supply (SMPS)[5] provided in most of the today electronic devices/equipment.
230V DC supply is given as an input instead of 230V AC, the Electro Magmatic Interference (EMI) filter in the first stage by-passes the input 230V DC and the output of the bridge rectifier is also HVDC near to 230V since drop in two diodes is1.2 volts only[4]. This HVDC is the prime power source for the SMPS circuit[5]. Therefore AC to DC SMPS is a DC to DC SMPS. The output DC voltages of the SMPS are constant for wide variation of input AC voltage and load current[5]. This is same for the variation of input DC voltage.
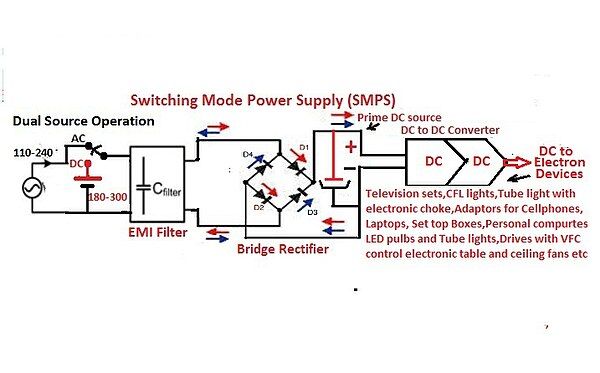
Also, if the input DC voltage polarity reversed, the HVDC polarity of the bridge rectifier output not changed. Hence the bridge rectifier is called as reverse voltage protection circuit..[5]
Application and advantages
[edit]The Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) feeds power from batteries[6] to the loads when the main supply failure. The best UPS system[6] has:
- Without interruption when feeding power to the loads during input power failure or low and higher input voltage situations.
- Less energy loss.
- Smaller in size.
- Reduced fabrication and installation cost.
- Good reliability and stability.
- Maintenance free.
- Easy to replace defective components with less effort and cost.
- Good quality (no harmonics).
Based on the basic principle operation of diodes[5], the HVDC power feed UPS system shares power to the electron devices (Load) from the grid formed with two sources through two diodes 1 and 2. Sources are
- Normal AC Supply rectified to DC
- HVDC Supply.
HVDC source will feed power to the load through the diode 2.[4] when normal AC failure. If HVDC from solar panels is connected to the grid through another diode 3 as a third source , solar energy can be utilized effectively[2][3]

Better efficiency and the requirements for UPS are achieved due to fewer power conversion stages (Sans Inverter) which incurred less energy loss than with an AC power feed.[7][8][1] International standardization of HVDC power feed technology is going on.[7][8][1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d "Trends in the International Standardization of HVDC Power Feeds". ResearchGate.
- ^ a b c "Enjoy uninterrupted power sans inverters, the way retired Madurai professor does". Times of India.
- ^ a b c "No more worries about the electricity bill... the 'microgrid' device has arrived!". Vikatan.
- ^ a b c d "Bridge Rectifier". Unacademy.
- ^ a b c d e f "Simple SMPS Circuit". Theory Circuit. 20 March 2024.
- ^ a b "Choosing a UPS System 101: The Fundamentals". 19 February 2018.
- ^ a b "SAN Switch". IBM.
- ^ a b "HVDC Power Supply System Implementation".

- in-depth (not just brief mentions about the subject or routine announcements)
- reliable
- secondary
- strictly independent of the subject
Make sure you add references that meet all four of these criteria before resubmitting. Learn about mistakes to avoid when addressing this issue. If no additional references exist, the subject is not suitable for Wikipedia.