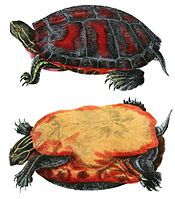
Red-eared slider
| Red-eared slider | |
|---|---|

| |
| At the Cincinnati Zoo | |

| |
| 1865 engraving by Karl Bodmer, who accompanied the authority on his expedition | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Superfamily: | Testudinoidea |
| Family: | Emydidae |
| Genus: | Trachemys |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | T. s. elegans
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Trachemys scripta elegans (Wied-Neuwied, 1839)
| |

| |
| The US native range T. s. elegans | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
The red-eared slider or red-eared terrapin (Trachemys scripta elegans) is a subspecies of the pond slider (Trachemys scripta), a semiaquatic turtle belonging to the family Emydidae. It is the most popular pet turtle in the United States, is also popular as a pet across the rest of the world, and is the most invasive turtle.[2] It is the most commonly traded turtle in the world.[3][4]
The red-eared slider is native from the Midwestern United States to northern Mexico, but has become established in other places because of pet releases, and has become invasive in many areas where it outcompetes native species. The red-eared slider is included in the list of the world's 100 most invasive species.[6]
Etymology
[edit]
The red-eared slider gets its name from the small, red stripe around its ears, or where its ears would be, and from its ability to slide quickly off rocks and logs into the water. This species was previously known as Troost's turtle in honor of an American herpetologist Gerard Troost. Trachemys scripta troostii is now the scientific name for another subspecies, the Cumberland slider.
Taxonomy
[edit]The red-eared slider belongs to the order Testudines, which contains about 250 turtle species. It is a subspecies of Trachemys scripta. It was previously classified under the name Chrysemys scripta elegans. Trachemys scripta contains three subspecies: T. s. elegans (red-eared slider), T. s. scripta (yellow-bellied slider), and T. s. troostii (Cumberland slider).[7]
Description
[edit]

The carapace of this species can reach more than 40 cm (16 in) in length, but the typical length ranges from 15 to 20 cm (6 to 8 in).[8] The females of the species are usually larger than the males. They typically live between 20–30 years, although some individuals can live for more than 40 years.[9] Their life expectancy is shorter when they are kept in captivity.[10] The quality of their living environment has a strong influence on their lifespans and well being.
The shell is divided into the upper or dorsal carapace, and the lower, ventral carapace or plastron.[2] The upper carapace consists of the vertebral scutes, which form the central, elevated portion; pleural scutes that are located around the vertebral scutes; and then the marginal scutes around the edge of the carapace. The rear marginal scutes are notched. The scutes are bony keratinous elements. The carapace is oval and flattened (especially in the male) and has a weak keel that is more pronounced in the young.[11] The color of the carapace changes depending on the age of the turtle. It usually has a dark green background with light and dark, highly variable markings. In young or recently hatched turtles, it is leaf green and gets slightly darker as a turtle gets older, until it is a very dark green, and then turns a shade between brown and olive green. The plastron is always a light yellow with dark, paired, irregular markings in the centre of most scutes. The plastron is highly variable in pattern. The head, legs, and tail are green with fine, irregular, yellow lines. The whole shell is covered in these stripes and markings that aid in camouflaging an individual.

These turtles also have a complete skeletal system, with partially webbed feet that help them to swim and that can be withdrawn inside the carapace along with the head and tail. The red stripe on each side of the head distinguishes the red-eared slider from all other North American species and gives this species its name, as the stripe is located behind the eyes, where their (external) ears would be. These stripes may lose their color over time.[10] Color and vibrance of ear stripe can indicate immune health, with bright red having higher immune response than yellow stripes.[12] Some individuals can also have a small mark of the same color on the top of their heads. The red-eared slider does not have a visible outer ear or an external auditory canal; instead, it relies on a middle ear entirely covered by a cartilaginous tympanic disc.[13]
Like other turtles, the species is poikilotherm and thus dependent on the temperature of its environment.[2] For this reason, it needs to sunbathe frequently to warm up and maintain body temperature.
Sexual dimorphism
[edit]

Some dimorphism exists between males and females.[14]
Red-eared slider young look practically identical regardless of their sex, making distinguishing them difficult. One useful method, however, is to inspect the markings under their carapace, which fade as the turtles age. Distinguishing the sex of adults is much easier, as the shells of mature males are smaller than those of females.[15] Male red-eared sliders reach sexual maturity when their carapaces' diameters measure 10 cm (3.9 in) and females reach maturity when their carapaces measure about 15 cm (5.9 in). Both males and females reach sexual maturity at 5–6 years old. Males are normally smaller than females, although this parameter is sometimes difficult to apply, as individuals being compared could be of different ages.
Males have longer claws on their front feet than the females; this helps them to hold onto a female during mating, and is used during courtship displays.[16] The males' tails are thicker and longer. Typically, the cloacal opening of a female is at or under the rear edge of the carapace, while the male's opening occurs beyond the edge of the carapace. The male's plastron is slightly concave, while that of the female is completely flat. The male's concave plastron also helps to stabilize the male on the female's carapace during mating.[17] Older males can sometimes have a dark greyish-olive green melanistic coloration, with very subdued markings. The red stripe on the sides of the head may be difficult to see or be absent. The female's appearance is substantially the same throughout her life.
Distribution and habitat
[edit]The red-eared slider originated from the area around the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico, in warm climates in the Southeastern United States. Their native areas range from the southeast of Colorado to Virginia and Florida. In nature, they inhabit areas with a source of still, warm water, such as ponds, lakes, swamps, creeks, streams, or slow-flowing rivers.
They live in areas of calm water, where they are able to leave the water easily by climbing onto rocks or tree trunks so they can warm up in the sun. Individuals are often found sunbathing in a group or even on top of each other. They also require abundant aquatic plants, as these are the adults' main food, although they are omnivores.[18] Turtles in the wild always remain close to water unless they are searching for a new habitat or when females leave the water to lay their eggs.
Invasive species
[edit]Invasive red-eared sliders cause negative impacts in the ecosystems they are introduced to because they have certain advantages over the native populations, such as a lower age at maturity, higher fecundity rates, and larger body size, which gives them a competitive advantage at basking and nesting sites, as well as when exploiting food resources.[19] They also transmit diseases and displace the other turtle species with which they compete for food and breeding space.[20]
Owing to their popularity as pets, red-eared sliders have been released or escaped into the wild in many parts of the world.[21] This turtle is considered one of the world's worst invasive species.[5] Feral populations are now found in Bermuda,[22] Canada,[23] Australia, Europe, Great Britain, South Africa, the Caribbean Islands, Israel, Bahrain, the Mariana Islands, Guam, Russia, and south- and far-east Asia.[24][25][26] Within Great Britain, red-eared sliders have a wide distribution throughout England, Scotland, and Wales.[27]
In Australia, it is illegal for members of the public to import, keep, trade, or release red-eared sliders, as they are regarded as an invasive species[28] – see below. Their import has also been banned by the European Union[29] as well as specific EU member countries.[30] In 2015, Japan announced it was planning to ban the import of red-eared sliders,[31] and officially established in June 2023. While this bans it and red swamp crayfish from importing, trading and releasing to wild, it is still able to keep it alive at home.[32][33]

Behavior
[edit]Red-eared sliders are almost entirely aquatic, but as they are cold-blooded, they leave the water to sunbathe to regulate their temperature.
Hibernation
[edit]Red-eared sliders do not hibernate, but actually brumate; while they become less active, they do occasionally rise to the surface for food or air. Brumation can occur to varying degrees. In the wild, red-eared sliders brumate over the winter at the bottoms of ponds or shallow lakes. They generally become inactive in October, when temperatures fall below 10 °C (50 °F).[11] During this time, the turtles enter a state of sopor, during which they do not eat or defecate, they remain nearly motionless, and the frequency of their breathing falls. Individuals usually brumate under water, but they have also been found under banks and rocks, and in hollow stumps. In warmer winter climates, they can become active and come to the surface for basking. When the temperature begins to drop again, however, they quickly return to a brumation state. Sliders generally come up for food in early March to as late as the end of April.

During brumation, T. s. elegans can survive anaerobically for weeks, producing ATP from glycolysis. The turtle's metabolic rate drops dramatically, with heart rate and cardiac output dropping by 80% to minimize energy requirements.[34][35] The lactic acid produced is buffered by minerals in the shell, preventing acidosis.[36] Red-eared sliders kept captive indoors should not brumate.
Reproduction
[edit]
Courtship and mating activities for red-eared sliders usually occur between March and July, and take place under water. During courtship, the male swims around the female and flutters or vibrates the back side of his long claws on and around her face and head, possibly to direct pheromones towards her.[37] The female swims toward the male, and if she is receptive, sinks to the bottom for mating. If the female is not receptive, she may become aggressive towards the male. Courtship can last 45 minutes, but mating takes only 10 minutes.[20]
On occasion, a male may appear to be courting another male, and when kept in captivity may also show this behaviour towards other household pets. Between male turtles, it could be a sign of dominance and may preclude a fight. Young turtles may carry out the courtship dance before they reach sexual maturity at 5 years of age, but they are unable to mate.[38]

After mating, the female spends extra time basking to keep her eggs warm.[38] She may also have a change of diet, eating only certain foods, or not eating as much as she normally would. A female can lay between two and 30 eggs depending on body size and other factors.[24] One female can lay up to 5 clutches in the same year, and clutches are usually spaced 12–36 days apart.[39] The time between mating and egg-laying can be days or weeks. The fertilization and laying can also be in conjunction, with eggs immediately laid [40] based on location and nutrients available. The actual egg fertilization takes place during the egg-laying. This process also permits the laying of fertile eggs the following season, as the sperm can remain viable and available in the female's body in the absence of mating. During the last weeks of gestation, the female spends less time in the water and smells and scratches at the ground, indicating she is searching for a suitable place to lay her eggs. The female excavates a hole, using her hind legs, and lays her eggs in it.[41]

Incubation takes 59–112 days.[24] Late-season hatchlings may spend the winter in the nest and emerge when the weather warms in the spring. Just prior to hatching, the egg contains 50% turtle and 50% egg sac. A new hatchling breaks open its egg with its egg tooth, which falls out about an hour after hatching. This egg tooth never grows back. Hatchlings may stay inside their eggshells after hatching for the first day or two. If they are forced to leave the eggshell before they are ready, they will return if possible. When a hatchling decides to leave the shell, it still has a small sac protruding from its plastron. The yolk sac is vital and provides nourishment while visible, and several days later, it will have been absorbed into the turtle's belly. The sac must be absorbed, and does not fall off. The split must heal on its own before the turtle is able to swim. The time between the egg hatching and water entry is 21 days.

Damage to or inordinate motion of the protruding egg yolk – enough to allow air into the turtle's body – results in death. This is the main reason for marking the top of turtle eggs if their relocation is required for any reason. An egg turned upside down will eventually terminate the embryo's growth by the sac smothering the embryo. If it manages to reach term, the turtle will try to flip over with the yolk sac, which would allow air into the body cavity and cause death. The other fatal danger is water getting into the body cavity before the sac is absorbed completely, and while the opening has not completely healed yet.
The sex of red-eared sliders is determined by the incubation temperature during critical phases of the embryos' development. Only males are produced when eggs are incubated at temperatures of 22–27 °C (72–81 °F), whereas females develop at warmer temperatures.[42] Colder temperatures result in the death of the embryos.
As pets, invasive species, and human infection risk
[edit]
Red-eared slider turtles are the world's most commonly traded reptile, due to their relatively low price, and usually low food price, small size, and easy maintenance.[4][43][44] As with other turtles, tortoises, and box turtles, individuals that survive their first year or two can be expected to live generally around 30 years. They present an infection risk; particularly of Salmonella.[43]
Infection risks and United States federal regulations on commercial distribution
[edit]
Reptiles are asymptomatic (meaning they suffer no adverse side effects) carriers of bacteria of the genus Salmonella.[45] This has given rise to justifiable concerns given the many instances of infection of humans caused by the handling of turtles,[46] which has led to restrictions in the sale of red-eared sliders in the United States. A 1975 U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulation bans the sale (for general commercial and public use) of both turtle eggs and turtles with a carapace length less than 4 in (10 cm). This regulation comes under the Public Health Service Act, and is enforced by the FDA in cooperation with state and local health jurisdictions. The ban was enacted because of the public-health impact of turtle-associated salmonellosis. Turtles and turtle eggs found to be offered for sale in violation of this provision are subject to destruction in accordance with FDA procedures. A fine up to $1,001 and / or imprisonment for up to one year is the penalty for those who refuse to comply with a valid final demand for destruction of such turtles or their eggs.[48] Many stores and flea markets still sell small turtles due to an exception in the FDA regulation that allows turtles under 4 in (10 cm) to be sold "for bona fide scientific, educational, or exhibition purposes, other than use as pets."[47] As with many other animals and inanimate objects, the risk of Salmonella exposure can be reduced by following basic rules of cleanliness. Small children must be taught to wash their hands immediately after they finish playing with the turtle, feeding it, or changing its water.
US state laws
[edit]Some states have other laws and regulations regarding possession of red-eared sliders because they can be an invasive species where they are not native and have been introduced through the pet trade. It is illegal in Florida to sell any wild-type red-eared slider, as they interbreed with the local yellow-bellied slider population, T. s. scripta, which is another subspecies of pond sliders, and hybrids typically combine the markings of the two subspecies. However, unusual color varieties such as albino and pastel red-eared sliders, which are derived from captive breeding, are still allowed for sale.[49]
Invasive status in Australia
[edit]In Australia, breeding populations have been found in New South Wales and Queensland, and individual turtles have been found in the wild in Victoria, the Australian Capital Territory, and Western Australia.[50]
Red-eared slider turtles are considered a significant threat to native turtle species; they mature more quickly, grow larger, produce more offspring, and are more aggressive.[50] Numerous studies indicate that red-eared slider turtles can out-compete native turtles for food and nesting and basking sites.[51] Unlike the general diet of pet red-eared sliders, wild red-eared sliders are usually omnivorous.[52] Because red-eared slider turtles eat plants as well as animals, they could also have a negative impact on a range of native aquatic species, including rare frogs.[53] Also, a significant risk exists that red-eared slider turtles can transfer diseases and parasites to native reptile species. A malaria-like parasite was spread to two wild turtle populations in Lane Cove River, Sydney.[54]
Social and economic costs are also likely to be substantial. The Queensland government has invested close to AU$1 million in eradication programs to date.[50] The turtle may also cause significant public-health costs due to the impacts of turtle-associated salmonella on human health. Outbreaks in multiple states and fatalities in children, associated with handling Salmonella-infected turtles, have been recorded in the US.[55] Salmonella can also spread to humans when turtles contaminate drinking water.[56]
The actions by state governments have varied considerably to date, ranging from ongoing eradication efforts by the Queensland government to very little action by the government of New South Wales.[57] Experts have ranked the species as high priority for management in Australia, and are calling for a national prevention and eradication strategy, including a concerted education and compliance program to stop the illegal trade, possession, and release of slider turtles.[59]
Invasive status in India
[edit]Red-eared slider turtles are threatening to invade the natural water bodies across northeast India, which are home to 21 out of 29 vulnerable native Indian species of freshwater turtle.[60] Between August 2018 and June 2019, a team of herpetologists from the NGO "Help Earth" found red-eared sliders in the Deepor Beel wildlife sanctuary and Ugratara Devalaya temple pond.[61] Further reports have been made from an unnamed stream, feeding into the Tlawng river, on a farm in the Mizoram capital, Aizawl.[citation needed]
In popular culture
[edit]Within the second volume of the Tales of the Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles, the popular comic-book heroes were revealed as specimens of the red-eared slider. The popularity of the Ninja Turtles, coupled with the release of the first live-action film, led to a craze for keeping them as pets in United Kingdom, with subsequent ecological havoc, as turtles were accidentally or deliberately released into the wild.[62]
See also
[edit]- Red-eared slider × yellow-bellied slider, an intergradation of a red-eared slider and yellow-bellied slider subspecies.
- Yellow-bellied slider
- Cumberland slider
References
[edit]- ^ Fritz Uwe; Peter Havaš (2007). "Checklist of Chelonians of the World". Vertebrate Zoology. 57 (2): 207–208. doi:10.3897/vz.57.e30895.
- ^ a b c Boylan Sánchez, Efrén (July–August 2003). "Las Tortugas". Ed. Antártida. Archived from the original on 20 June 2008. Retrieved 20 July 2007.
- ^ "Senda tuxtlas". Especies. Acuario de Veracruz. Archived from the original on 4 July 2007. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ a b Herrel, Anthony; van der Meijden, Arie (1 April 2014). "An analysis of the live reptile and amphibian trade in the USA compared to the global trade in endangered species". The Herpetological Journal. 24 (2): 103–110.
- ^ a b Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; de Poorter, M. (November 2004) [2000]. 100 of the world's worst invasive alien species: A selection from the Global Invasive Species Database (PDF). The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) of the Species Survival Commission (SSC) (Report) (Updated and reprinted ed.). International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 December 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2017.
See also original edition: Lowe, Browne, et al. (2000).[6] - ^ a b Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S. (2000). 100 of the world's worst invasive alien species: A selection from the Global Invasive Species Database. IUCN/SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) (Report). Auckland, New Zealand: International Union for Conservation of Nature.
See also updated edition: Lowe, Browne, et al. (2004).[5] - ^ Win Kirkpatrick, Amanda Page & Massam, Marion (November 2007). Pond slider (Trachemys scripta) risk assessments for Australia (PDF) (Report). Department of Agriculture and Food. Government of Western Australia.
- ^ "La tortuga de Florida". Tortugas. belonweb.com. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ "Tortuga de orejas rojas". Archived from the original on 27 October 2007. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ a b "Tortuga de orejas rojas". es.vivapets.com (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 11 July 2007. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ a b Rodríguez Garrido, María del Carmen. "Tortugas en estanques de jardín" [Turtles in garden ponds]. elestanque.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ Polo-Cavia, Nuria; López, Pilar; Martín, José (2013). "Head coloration reflects health state in the red-eared slider Trachemys scripta elegans". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 67 (1): 153–162. Bibcode:2013BEcoS..67..153P. doi:10.1007/s00265-012-1435-z. ISSN 0340-5443. JSTOR 23360179. S2CID 253807552.
- ^ Christensen-Dalsgaard, Jakob; Brandt, Christian; Willis, Katie L.; Christensen, Christian Bech; Ketten, Darlene; Edds-Walton, Peggy; et al. (2012). "Specialization for underwater hearing by the tympanic middle ear of the turtle, Trachemys scripta elegans". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 279 (1739): 2816–2824. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.0290. PMC 3367789. PMID 22438494.
- ^ "Tachemys scripta". UM Museum of Zoology. Animal Diversity Web (Animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu). Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan. Retrieved 16 March 2010.
- ^ Gibbons, J. Whitfield & Lovich, Jeffery E. (1990). "Sexual dimorphism in turtles, with emphasis on the slider turtle (Trachemys scripta)" (PDF). Herpetological Monographs. 4: 1–29. doi:10.2307/1466966. JSTOR 1466966. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 November 2013.
- ^ Mohan-Gibbons, Hm & Norton, T. (2010). "Turtles, tortoises and terrapins". In Tynes, V.V. (ed.). Behaviour of Exotic Pets. Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8138-0078-3 – via Google Books.
- ^ O'Rourke, D.P.; Schumacher, J. (2002). "Biology and Diseases of Reptiles". In Fox, James G.; Anderson, Lynn C.; Loew, Franklin M.; Quimby, Fred W. (eds.). Laboratory Animal Medicine. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-263951-7 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Red-eared slider turtle". Encyclopaedia of North American Reptiles and Amphibians. Mobile Reference. 15 December 2009. ISBN 978-1605014593.
- ^ Parry, B. (2009). "The red-eared slider and hickatee on Grand Cayman". Testudo. British Chelonia Group. Retrieved 26 September 2013.
- ^ a b Pendlebury, Paul; Bringsøe, H.; Pendelbury, Paul (2006). Trachemys scripta. NOBANIS – Invasive Alien Species Fact Sheet. Global Invasive Species Database (Report). IUCN/SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG). International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Archived from the original on 13 March 2016. Retrieved 17 August 2009.
- ^ "Turtle mania causes welfare headache". Scotland. BBC News. 7 April 2000. Retrieved 28 February 2009.
- ^ "Red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans)". Department of Environment and Natural Resources. The Government of Bermuda. Retrieved 3 October 2021.
- ^ "Red-eared slider". Canadian Wildlife Federation. 2021. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ a b c Scalera, Riccardo (2020). "Trachemys scripta" (PDF). europe-aliens.org. Europe Aliens. doi:10.15468/ybwd3x. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
Delivering alien invasive species inventories for Europe
- ^ Kikillus, K. Heidy; Hare, K.M.; Hartley, S. (1 December 2010). "Minimizing false-negatives when predicting the potential distribution of an invasive species: A bioclimatic envelope for the red-eared slider at global and regional scales". Animal Conservation. 13: 5–15. Bibcode:2010AnCon..13S...5H. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1795.2008.00299.x. ISSN 1469-1795.
- ^ Reshetnikov, Andrey N. (24 January 2023). "Rarely naturalized, but widespread and even invasive: the paradox of a popular pet terrapin expansion in Eurasia". NeoBiota. 81 (1): 91–127. doi:10.3897/neobiota.81.90473. Retrieved 20 February 2023.
- ^ Allain, Steven J. R. "Mining Flickr: a method for expanding the known distribution of invasive species" (PDF). Herpetological Bulletin. 148: 11–14.
- ^ Red-eared slider (PDF) (Report). Animal Pest Alert. Vol. 6. Western Australia: Department of Agriculture. 2009.
- ^ Species listed in the Annexes of the EU Wildlife Trade Regulations. European Commission Environment (Report). 16 September 2013. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- ^ Capdevila Argüelles, Laura; Iglesias García, Ángela; Orueta, Jorge F.; Zilletti, Bernardo (2006). "Lista negra preliminar de EEI para España" (PDF). Especies Exóticas Invasoras: Diagnóstico y bases para la prevención y el Manejo [Invasive Exotic Species: Diagnostics and basēs for their prevention and management]. Organismo Autónomo Parques Nacionales. Madrid, ES: Ministerio de Medio Ambiente. ISBN 978-84-8014-667-8.
- ^ "Japan to ban imports of red-eared slider turtles". The Japan Times. 30 July 2015. Archived from the original on 11 April 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
- ^ "Import, sale ban on alien species wreaking havoc on ecosystems | The Asahi Shimbun: Breaking News, Japan News and Analysis". The Asahi Shimbun. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 6 January 2025.
- ^ "News Navigator: As Japan clamps down on invasive crayfish, turtles, what are rules on pets?". Mainichi Daily News. 21 January 2023. Retrieved 6 January 2025.
- ^ Hicks, J.M.; Farrell, A.P. (2000). "The cardiovascular responses of the red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta) acclimated to either 22 or 5 degrees C. – I. Effects of anoxic exposure on in vivo cardiac performance". The Journal of Experimental Biology. 203 (Pt 24): 3765–3774. doi:10.1242/jeb.203.24.3765. PMID 11076774.
- ^ Hicks, J.M.; Farrell, A.P. (2000). "The cardiovascular responses of the red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta) acclimated to either 22 or 5 degrees C. – II. Effects of anoxia on adrenergic and cholinergic control". The Journal of Experimental Biology. 203 (Pt 24): 3775–3784. doi:10.1242/jeb.203.24.3775. PMID 11076740.
- ^ Krivoruchko, A.; Storey, K.B. (2010). "Forever young: Mechanisms of natural anoxia tolerance and potential links to longevity". Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 3 (3): 186–198. doi:10.4161/oxim.3.3.12356. PMC 2952077. PMID 20716943.
- ^ Chitty, J. & Raftery, A. (2013). "Biology". Essentials of Tortoise Medicine and Surgery. Wiley Blackwell. p. 38. ISBN 978-1-4051-9544-7.
- ^ a b "Reproducción". reslider.free.fr. Archived from the original on 25 December 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ Ernst; et al. "Trachemys scripta". Nlbif.eti.uva.nl. Turtles of the World. Amsterdam, NL: Universiteit van Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 16 March 2010.
- ^ Tucker, John K.; Paukstis, Gary L.; Janzen, Fredric J. (1998). "Annual and Local Variation in Reproduction in the Red-Eared Slider, Trachemys scripta elegans". Journal of Herpetology. 32 (4): 515–526. doi:10.2307/1565205. ISSN 0022-1511. JSTOR 1565205.
- ^ Loza, V. Antonio. "Trachemys scripta elegans (Tortuga de orejas rojas)". Archived from the original on 17 July 2007. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ Washington NatureMapping Program, Animal Facts: Red-eared Slider. Retrieved: 2012-11-13.
- ^ a b Csurhes, S.; Hankamer, C. (2012). Red-eared slider turtle. Invasive species risk assessment (Report). Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry. Government of Queensland.
- ^ "Introduction – Is a slider right for you?". Slider Guide. Turtle Source (Turtlesource.webs.com). Archived from the original on 6 December 2009. Retrieved 6 December 2009.
- ^ Iglesias, Isabel. "Tortuga de orejas rojas". tiendanimal.es. Retrieved 21 July 2007.
- ^ "Multistate outbreak of human salmonella infections associated with exposure to turtles 2007–2008". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (CDC MMWR). 57 (3). United States: Centers for Disease Control: 69–72. 25 January 2008.
- ^ a b Turtles intrastate and interstate requirements (Report). FDA Regulation. Sec. 1240.62, page 678 part d1.
- ^ ""4 Inch Law", actually an FDA regulation". FAQ. GCTTS.
See also [47] - ^ "Turtle ban begins today". newszap.com. New state law. 1 July 2007. Retrieved 6 July 2007.
- ^ a b c Csurhes, S.; Hankamer, C. (2016) [2012]. Red-eared slider turtle (PDF). Invasive animal risk assessment (Report). Biosecurity Queensland (updated ed.). Queensland, AU: Queensland Government. Retrieved 29 May 2017.
- ^ Polo-Cavia, N.; López, P.; Martín, J. (2010). "Competitive interactions during basking between native and invasive freshwater turtle species". Biological Invasions. 12 (7): 2141–2152. Bibcode:2010BiInv..12.2141P. doi:10.1007/s10530-009-9615-0. S2CID 37769857.
- ^ Prevot-Julliard, A. C.; Gousset, E.; Archinard, C.; Cadi, A.; Girondot, M. (2007). "Pets and invasion risks: is the Slider turtle strictly carnivorous?". Amphibia-Reptilia. 28 (1): 139–143. doi:10.1163/156853807779799036.
- ^ O'Keefe, S. (2005). Investing in conjecture: Eradicating the red-eared slider in Queensland. 13th Australasian Vertebrate Pest Conference. Wellington, New Zealand.
- ^ Red-eared slider: Social and economic impacts. Department of Agriculture and Food (Report). Animal pest alert. Vol. 6/2009. Western Australia. 2009.
- ^ "Turtle associated salmonellosis in humans". United States 2006–2007. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (CDC MMWR). 56 (26). United States: Center for Disease Control: 649–652. 2007.
- ^ Bomford, M. (2008). Risk assessment models for establishment of exotic vertebrates in Australia and New Zealand (Report). Canberra, ACT, Australia: Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Centre.
- ^ a b Red-eared slider turtles (PDF) (Report). Biosecurity Failures in Australia. Australia: Invasive Species Council. 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2017.
- ^ Massam, M.; Kirkpatrick, W.; Page, A. (2010). Assessment and prioritisation of risk for forty introduced animal species (Report). Canberra, AU: Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Centre.
- ^ For example see[57] and [58]
- ^ Karmakar, Rahul (15 May 2021). "Native Indian turtles face U.S. slider threat across northeast". The Hindu.
- ^ Purkayastha, J.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Bohra, S. C. (2020). "First record of the exotic red-eared slider, Trachemys scripta elegans (Wied 1838) (Emydidae) from Assam, India". Reptiles & Amphibians. 27 (2): 286–287. doi:10.17161/randa.v27i2.14370.
- ^ "'Hero Turtle' craze leads to duck deaths". England. BBC News. 16 November 2001. Retrieved 28 February 2009.
Further reading
[edit]- Bowden, Rachel M. (September–October 2009). "A Modified Yolk Biopsy: Technique improves survivorship of turtle eggs". Physiological and Biochemical Zoology. 82 (5). Cal State East Bay Press: 611–615. doi:10.1086/596579. ISSN 1522-2152. PMID 19193061. S2CID 25913137. (online copy, p. 216, at Google Books)
- Ernst, Carl H.; Lovich, Jeffrey E. (2009). Turtles of the United States and Canada. Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 444–470. ISBN 978-0-8018-9121-2. (online copy, p. 444, at Google Books)
- Harding, James H. (1997). Amphibians and Reptiles of the Great Lakes Region. University of Michigan Press. pp. 216–220. ISBN 0-472-06628-5. (online copy, p. 216, at Google Books)
- Jensen, John B.; Camp, Carlos D.; Gibbons, Whit (2008). Amphibians and Reptiles of Georgia. University of Georgia Press. pp. 500–502. ISBN 978-0-8203-3111-9. (online copy, p. 500, at Google Books)
External links
[edit]- "Red-eared slider". Guides. Animal Planet. Discovery Channel.
- "Exotic pets". — information on aquatic turtles & tortoises including a few articles specific to red-eared sliders
- "Red-eared slider". Natural History. Gulf Coast Turtle & Tortoise Society.
- "Red-eared slider". RedEarSider.com (main page). — a site about caring for turtles in captivity
- "Red-Eared Slider (Trachemys scripta elegans)". Species Profile. National Invasive Species Information Center. United States National Agricultural Library.
- "Red-eared slider turtle". Business Department. Government of Queensland. 1 July 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2021.