Charles Harington (British Army officer, born 1872)
Sir Charles Harington | |
|---|---|
 As a lieutenant-colonel in London, 1915 | |
| Nickname(s) | "Tim" "Harington of Chanak" |
| Born | 31 May 1872 Chichester, England |
| Died | 22 October 1940 (aged 68) Cheltenham, England |
| Allegiance | United Kingdom |
| Service | British Army |
| Years of service | 1892–1938 |
| Rank | General |
| Service number | 23005[1] |
| Unit | King's Regiment (Liverpool) |
| Commands | Aldershot Command Western Command, India Northern Command |
| Battles / wars | Second Boer War First World War |
| Awards | Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the British Empire Distinguished Service Order |
| Relations | General Charles Henry Pepys Harington |
| Other work | Governor of Gibraltar General Harington Cup |
General Sir Charles Harington Harington (31 May 1872 – 22 October 1940) was a British Army officer most noted for his service during the First World War and the Chanak Crisis. During his 46 years in the army, Harington served in the Second Boer War, held various staff positions during the First World War, served as Deputy Chief of the Imperial General Staff between 1918 and 1920, commanded the occupation forces in the Black Sea and Turkey, and ultimately became Governor of Gibraltar in 1933.
Respected by his peers and remembered as an "outstanding soldier", Harington served the entirety of the First World War in a staff capacity, most notably as Chief of Staff to General Herbert Plumer, commander of the Second Army, with whom he had a strong mutual understanding.[2][3] As Commander-in-Chief of the Allied occupation army, based in Constantinople (Dersaadet İşgal Orduları Başkumandanı General Harington in Ottoman Turkish), Harington was instrumental in averting a war between the United Kingdom and pre-republic Turkey.[4]
Harington retired in 1938, having been Governor of Gibraltar since May 1933. His association with the British Army in retirement was facilitated by symbolic positions, such as honorary colonel of the regular King's Regiment, its territorial 7th Battalion, and the 4/15th Punjab Regiment.[5]
Early life
[edit]Harrington was born in Chichester, the son of Emanuel Thomas Poë and Isabella Jane (née Crowdy), and christened Charles Harington.[6] Of Anglo-Irish heritage, Harington gained his unusual name repetition as a four-year-old infant, when his father replaced the family's original surname of "Poë" with the maiden name of Charles's grandmother.[7] His nickname of "Tim", by which he was almost universally known, was acquired while on his inaugural deployment abroad. Fellow officers from his battalion assigned Harington this nickname while en route to Aden after learning of the conviction of Timothy Charles Harrington, an Irish nationalist and Member of Parliament.[8]
Educated privately and at Gresson's School in Worthing, Harington continued his studies at Cheltenham College. An interest in sports, particularly cricket and swimming, developed during his school years.[9] He was admitted into Sandhurst in 1890 and after graduation two years later was commissioned as a second lieutenant into the 2nd Battalion the King's Liverpool Regiment on 9 January 1892.[9] He was promoted to lieutenant on 4 February 1893, and became its adjutant in 1897. After the outbreak of the Second Boer War in late 1899, Harington was seconded as a railway staff officer in South Africa, and was promoted to captain on 21 March 1900.[10][11] For his service in the war, Harison was decorated with the Distinguished Service Order (DSO),[12] and he was characterised in a despatch as being "an officer of first-rate ability, business capacity and tact".[13]
Recalled as adjutant of the 4th King's Regiment, Harington served with the battalion in Ireland for about a year under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Grattan (his future father-in-law). He was reassigned, with Colonel Grattan, to the 13th Provisional Battalion after the disbandment of the 4th and later rejoined the 2nd King's at the Curragh as adjutant from 11 September 1902.[14][15] Harington returned to Sandhurst as commanding officer of Gentleman Cadets in 1903. The appointment lasted almost four-years and entailed him being responsible for the instruction of officer cadets.[16] He was selected for employment at Staff College, Camberley in 1906 – a decision that had neither been anticipated or sought[17] – and later moved to the War Office and Army Headquarters.[18][19] Harington transferred to Aldershot in 1911 to assume the position of brigade major to the 6th Infantry Brigade, which consisted of the 1st King's and five other battalions.[20]
First World War
[edit]1914
[edit]War was declared by Britain on 4 August 1914 after the invasion of Belgium by the German Empire, which, with Austria-Hungary, was in conflict with France, Russia, and Serbia. Harington had been attached to the Mobilisation Branch of the War Office since July and did not venture outside for ten days.[21] He witnessed the departure of his regiment, the 1st King's, from Talavera Barracks on 12 August. In his foreword to Everard Wyrall's History of the King's Regiment (Liverpool) 1914–19, Harington recalled his inspection of the battalion five years later, in Cologne, Germany,
Of the 1,000 officers, non-commissioned officers and men I had seen start out from Aldershot in August, 1914, on that journey, not a single officer and barely a handful of non-commissioned officers and men remained, and yet the battalion had won through. There were the Colours before me with their pre-war Honours on them. How many new ones had they earned? My heart was too full to say much to the battalion. My greatest friends, my brother officers, all my old company except one or two, had gone; the majority had made the supreme sacrifice....[22]
The British Expeditionary Force began to reorganise immediately after the Battle of Mons and subsequent retreat to the Marne. Harington became General Staff Officer, Grade II (GSO2) in III Corps, formed under Lieutenant-General William Pulteney to group the 4th and 6th divisions.[23]
1915
[edit]Two months after promotion to brevet lieutenant colonel, Harington joined the 49th (West Riding) Division as GSO1 in April 1915.[24] While positioned in the Ypres Salient, the 49th's commanding officer, Major General Thomas Baldock, was seriously wounded and replaced by Major General Edward Perceval. His later incapacitation by influenza burdened Harington, one of the few regulars in the division, with most of Perceval's responsibilities.[25] Months later, Harington learnt that Perceval's absence had necessitated his retention, precluding his transfer to Salonika to serve with XII Corps.[26] Expecting to assume command of a brigade in the 14th (Light) Division after five days of leave in September, having been informed of such a prospect by General Plumer, Harington was notified on his return that he was instead being transferred to the Canadian Corps as Brigadier General, General Staff (BGGS).[25]
1916
[edit]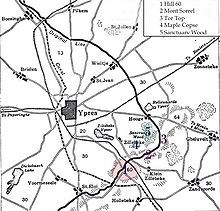
The Canadian Corps had been constituted in September after the arrival of the 2nd Canadian Division. When formed under the command of Lieutenant General Edwin Alderson, the corps lacked a general staff and consisted of an infantry division and cavalry brigade. Alderson was succeeded in May 1916 by General Sir Julian Byng, who presided over his first battle as corps commander, just weeks after his appointment. Allocated positions in the Ypres Salient near Hooge, Hill 60 and Zwarteleen, the Canadian Corps had been instructed by Byng to begin preparations for a "localised attack" not anticipating the possibility of one being conducted by the German XIII Corps against the tactically important vantages Mount Sorrel and Tor Top.[27][28]
The German bombardment intensified on the morning of 2 June, coinciding with a reconnoitring visit to the Canadian front line by Major General Malcolm Mercer and Brigadier General Williams, respective commanders of the 3rd Canadian Division and 8th Brigade. Both were among 8,430 officers and other ranks who became casualties during the Battle of Mount Sorrel; Mercer was killed by shellfire and Williams severely wounded and taken prisoner.[28] Four mines opposite Mount Sorrel were detonated at about 1:00 p.m. before an assault by six infantry battalions, which displaced the remnants of the 1st and 4th Mounted Rifles and Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry from their devastated trenches. The first Canadian counter-attack, executed on 3 June, was deficiently organised and coordinated, resulting in heavy casualties and the removal of numerous officers.[29]
Byng was informed during the battle that Harington had been chosen to become a major general, General Staff (MGGS), in effect chief of staff, to General Plumer at Second Army headquarters, in succession to Major General Hugh Bruce Williams. Plumer visited Harington following the announcement, quipping "I won't have you at all unless you get Mt. Sorrel back!"[30] The recapture of the lost territory before the commencement of the Battle of the Somme became a priority for the Canadian Corps. Preparations for the second counter-attack, described by Harington as being "very careful", were meticulous and complete by 11 June.[28][31]
1917
[edit]As General Plumer's chief of staff, on the day before the Battle of Messines, Harington, who had been created a Companion of the Order of the Bath in January 1917,[32] famously said to reporters,
Gentlemen, I don’t know whether we are going to make history tomorrow, but at any rate we shall change geography.
At dawn the next day, June 7th, the largest man made explosion on earth shook the air as 19 mines filled with explosives detonated in front of the lines of the Second Army, killing approximately 10,000 Germans. The ensuing fight was a prelude to the Flanders Offensive of 31 July 1917.[33]
Later life
[edit]His tenure as Deputy Chief of the Imperial General Staff, subordinate to Field Marshal Sir Henry Wilson, encompassed the Irish War of Independence and civil unrest in India, punctuated by the Jallianwala Bagh massacre of Indian demonstrators at Amritsar by troops under the command of Brigadier General Reginald Dyer. Supporters of Dyer, mostly imperialist conservative "diehards", army officers and Ulster Unionists, opposed any form of disciplinary action being taken against the brigadier, whom they considered a defender of the British Empire.[34] Dyer continued to receive support from the highest echelons of the Army, most prominently Wilson, Harington and the Army Council.[35] According to Nigel Collet, in his book Butcher of Amritsar, Harington's schedule afforded him limited opportunity to comprehensively study Dyer's statement detailing his account while he did not "appear to have read any other document on the case".[35] Harington's own judgement conflicted with that of the government and corresponded more closely with that of Dyer.[35] Under pressure from the Secretary of State for War Winston Churchill,[36] the Army Council recommended that Dyer not receive further employment or promotion but elected not to publicly endorse compulsory retirement.[37]

After relinquishing his position as DCIGS to General Sir Philip Chetwode in 1920, Harington assumed command of the Army of the Black Sea, occupying parts of Turkey and later used to enforce a neutral zone established by the nominal signing of the Treaty of Sèvres during the Greco-Turkish War. Succeeding General Milne, Harington had under his command the British 28th Division at Istanbul, a Greek division at İzmit and a Greek regiment at Beykoz.[38] Additional contingents supplied by the French and Italian armies, under General Charpy and General Mombelli respectively, were subordinated to Harington when he became C-in-C, Allied Occupation Forces in Turkey.[39] In 1921, the Greek Army in Anatolia initiated an offensive against Mustafa Kemal's forces and maintained their advance with the intent of capturing Angora. Some 50,000 Greeks were redeployed to Eastern Thrace, threatening Istanbul. Harington later recalled in his memoir that during a social event, Turkish officials offered some 20,000 of its soldiers to defend the city, less than a year before the Chanak Crisis that prompted Greece to offer the assistance of 20,000 of its troops.[40]
Harington succeeded General Sir Ivor Maxse as general officer commanding-in-chief (GOC-in-C) of Northern Command in November 1923,[41] then GOC-in-C Western Command in 1927, when he received a promotion to the rank of full general,[42] and General Officer Commanding Aldershot Command in June 1931,[43] before becoming Governor of Gibraltar from 1933 during the Spanish Civil War.[44]
With his former commander, Plumer, Harington attended the unveiling of the Menin Gate on 24 July 1927.[45] Harington published two memoirs: Plumer of Messines (1935) and his autobiography, Tim Harington Looks Back (1940). He died at the age of 68, following his retirement, in Cheltenham, England.[46]
References
[edit]- ^ "No. 35047". The London Gazette. 17 January 1941. p. 402.
- ^ Bourne, J. M. (2003), Who's Who in World War One, p. 123
- ^ Holmes, Richard (2005), Tommy: The British Soldier on the Western Front 1914–1918, p. 232
- ^ Wrigley , Chris (2003), A Companion to Early Twentieth-Century Britain, p. 159
- ^ Mills, T.F. (2006), The King's Regiment (Liverpool), regiments.org. Retrieved on 15 January 2008. Archived 28 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Powell, Geoffrey S. (September 2004). "Harington , Sir Charles (1872–1940)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (May 2006 ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/33712. Retrieved 24 January 2008. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.) (subscription required)
- ^ Harington (1940), pp. 1–2
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 9
- ^ a b Harington (1940), p. 2
- ^ "No. 27175". The London Gazette. 20 March 1900. p. 1878.
- ^ Hart′s Army list, 1903
- ^ "No. 11296". The Edinburgh Gazette. 23 April 1901. p. 467.
- ^ "No. 27282". The London Gazette. 8 February 1901. p. 970.
- ^ "No. 27474". The London Gazette. 16 September 1902. p. 5961.
- ^ Harington (1940), pp. 26–27
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 30
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 29
- ^ Liddell Hart Centre for Military Archives, Gen Sir Charles Harington (1872–1940), King's College London. Retrieved on 16 January 2008.
- ^ "No. 28314". The London Gazette. 3 December 1909. p. 9231.
- ^ Harington (1940) p. 36
- ^ Harington (1940), pp. 38–9
- ^ Wyrall, Everard (2002), History of the King's Regiment (Liverpool) 1914–19, p. vi
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 41
- ^ "No. 29074". The London Gazette (Supplement). 16 February 1915. p. 1686.
- ^ a b Harington (1940), p .45
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 46
- ^ Harington (1940), pp. 47–48
- ^ a b c Baker, Chris, The Battle of Mount Sorrel 1916, 1914–1918.net. Retrieved on 22 January 2008. Archived 17 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ 2 PPCLI – WW1, army.forces.gc.ca. Retrieved on 29 January 2008. Archived 9 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 48
- ^ Harington, 1940, p. 48
- ^ "No. 29886". The London Gazette (Supplement). 29 December 1916. p. 2.
- ^ "This Explosion Was the Biggest Blast Before Atomic Bombs". National Geographic. 6 June 2017. Archived from the original on 12 April 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2022.
- ^ Thompson, Andrew (2005), The Empire Strikes Back?: The Impact of Imperialism on Britain From The Mid-Nineteenth Century, p. 135
- ^ a b c Collett, Nigel (2006), The Butcher of Amritsar, p. 373
- ^ Bose, Purnima (2003), Organizing Empire: Individualism, Collective Agency, and India, p. 44
- ^ Collett, Nigel (2006), The Butcher of Amritsar: General Reginald Dyer, pp. 373–74
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 100
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 108
- ^ Harington (1940), p. 109
- ^ "No. 32877". The London Gazette. 6 November 1923. p. 7551.
- ^ "No. 33255". The London Gazette. 8 March 1927. p. 1524.
- ^ "No. 33732". The London Gazette. 3 July 1931. p. 4341.
- ^ Liddell Hart Centre for Military Archives
- ^ The Menin Gate Memorial Inauguration, greatwar.co.uk. Retrieved on 17 January 2008.
- ^ "Milestones, Nov. 4, 1940". Time. 4 November 1940. Archived from the original on 29 March 2007. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
Sources
[edit]- Harington, Charles Harington, (1940), Tim Harington Looks Back, J Murray
External links
[edit]- Duffy, Michael (2001), Who's Who: Charles Harington, firstworldwar.com. Retrieved on 15 January 2008.
- Generals' Nicknames – No99: 'Tim' Harington, firstworldwar.bham.ac.uk. Retrieved on 15 January 2008.
- Liddell Hart Centre for Military Archives, Gen Sir Charles Harington (1872–1940), kcl.ac.uk. Retrieved on 16 January 2008.
- 1872 births
- 1940 deaths
- British Army generals
- People from Chichester
- People educated at Cheltenham College
- Free Foresters cricketers
- Graduates of the Royal Military College, Sandhurst
- Governors of Gibraltar
- British Army generals of World War I
- British Army personnel of the Second Boer War
- King's Regiment (Liverpool) officers
- English people of Irish descent
- Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the British Empire
- Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath
- Companions of the Distinguished Service Order
- Military personnel from Chichester


