Wilson's warbler
| Wilson's warbler | |
|---|---|

| |
| Adult male | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Parulidae |
| Genus: | Cardellina |
| Species: | C. pusilla
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cardellina pusilla (Wilson, A, 1811)
| |
| |
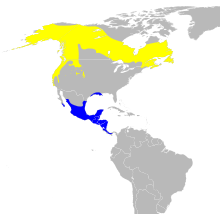
| Range of C. pusilla Breeding range Wintering range
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Muscicapa pusilla (protonym) | |
Wilson's warbler (Cardellina pusilla) is a small New World warbler. It is greenish above and yellow below, with rounded wings and a long, slim tail. The male has a black crown patch; depending on the subspecies, that mark is reduced or absent in the female. It breeds across Canada and south through the western United States, and winters from Mexico south through much of Central America. It is a very rare vagrant to western Europe.
Taxonomy
[edit]Wilson's warbler was formally described in 1811 by the ornithologist Alexander Wilson under the binomial name Muscicapa pusilla.[2] The type locality is southern New Jersey.[3] The species was moved to the genus Wilsonia by the naturalist and ornithologist Charles Lucien Bonaparte in 1838. Zoologist Thomas Nuttall moved it to Sylvania in 1840, and by 1845, many authors included it in Myiodioctes. In 1899, the American Ornithological Union returned the species to Wilsonia.[4] The species is currently assigned to the genus Cardellina.[5] The genus name Cardellina is a diminutive of the Italian dialect Cardella, a name for the European goldfinch, and the specific epithet pusilla means "very small".[6]
There are three recognized subspecies:[7]
- C. p. pusilla was described by Alexander Wilson in 1811.[8]
- C. p. pileolata was described by German naturalist Peter Simon Pallas in 1811.[8]
- C. p. chryseola was described by Robert Ridgway in 1902.[8]
The chryseola subspecies, which nests in northern coastal California to southwestern coastal Canada, has a distinctive orange-tinged yellow forehead. The population of the subspecies has declined sharply in the 21st century because it migrates preferentially to the southern end of the Baja Peninsula in Mexico,[9] where luxury resort and residential developments have replaced the bird's habitat.[10]
Description
[edit]
Wilson's warbler is a small passerine, ranging from 10 to 12 cm (3.9 to 4.7 in) in length, with a wingspan of 14–17 cm (5.5–6.7 in) and a mass of 5–10 g (0.18–0.35 oz).[11] It has a plain green-brown back and yellow underparts. The male has a small black cap. Males of the western race C. p. chryseola are greener above and brighter than males of the eastern, nominate race. Individuals from Alaska and the west-central portion of the species' range average slightly larger than those found in eastern and Pacific coastal populations.[11] Its song is a chattering series of loud descending notes. The call is a flat "chuff".[12]
Wilson's warbler resembles the yellow warbler: the latter is readily distinguished by its different shape, yellow wing markings, and yellow tail spots.[13]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]The breeding habitat is fairly open woodland with undergrowth or shrubs and thickets in moist areas with streams, ponds, bogs, and wet clearings.[12] Wilson's warbler breeds in northern Canada and the western US; it winters in overgrown clearings and coffee plantations,[12] forest edges, deciduous forests, tropical evergreens, pine-oak forests, mangroves, thorn-scrub, riparian gallery forests, brushy fields, and mixed forests . At all seasons, it prefers secondary growth, riparian habitats, lakes, montane and boreal forests with overgrown clearcuts. It is a very rare vagrant to Western Europe.[11]
Behavior and ecology
[edit]Breeding
[edit]Nesting generally begins in early March in west coast populations, and extends into August in the northern range.[12] The female does the majority of the nest building. The cup nest is typically constructed of vegetation and lined with grasses and hair. It is often sunken into moss or sedges at the base of shrubs.[12] The clutch varies from 2 to 7 eggs, which are creamy or off-white with fine reddish spots. The young are altricial.[11] The montane populations generally have a higher clutch size and nest success rate than those on the coast.[12] The eggs hatch at 11–15 days and the young fledge at 8–13 days; adults care for them for several weeks. Some montane populations are polygamous (one male breeds with multiple females).[12] Wilson's warbler is a frequent host for the brown-headed cowbird.[12]
Feeding
[edit]Wilson's warbler is an insectivore, feeding primarily on insects gleaned from leaves and twigs, or caught by flycatching.[14] Some of these insects include beetles, bees, or caterpillars. Wilson's warbler is an active forager, moving rapidly through shrubs, on the ground, and sometimes in taller trees during the winter.[12] Feeding birds often twitch their tails or flick their wings nervously.[15] The observed feeding rate of the male Wilson's warbler was not significantly different between males with or without mates.[16] It also eats a few berries.[11]
References
[edit]- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Cardellina pusilla". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22721879A94737104. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22721879A94737104.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Wilson, Alexander (1811). American Ornithology; or, the Natural History of the Birds of the United States: Illustrated with Plates Engraved and Colored from Original drawings taken from Nature. Vol. 3. Philadelphia: Bradford and Inskeep. p. 103, Plate 26 fig. 4.
- ^ Paynter, Raymond A. Jr, ed. (1968). Check-List of Birds of the World. Vol. 14. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Museum of Comparative Zoology. pp. 50–51.
- ^ Barrows, Walter Bradford (1912). Michigan Bird Life. East Lansing: Michigan Agricultural College. p. 685.
- ^ Chesser, R. Terry; Banks, Richard C.; Barker, F. Keith; Cicero, Carla; Dunn, Jon L.; Kratter, Andrew W.; Lovette, Irby J.; Rasmussen, Pamela C.; Remsen, J. V.; Rising, James D.; Stotz, Douglas F.; Winker, Kevin (2011). "Fifty-second supplement to the American Ornithologists' Union check-list of North American birds". The Auk. 128 (3): 600–613. doi:10.1525/auk.2011.128.3.600. S2CID 13691956.
- ^ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London, United Kingdom: Christopher Helm. pp. 91, 325. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (2020). "New World warblers, mitrospingid tanagers". IOC World Bird List Version 10.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ a b c "ITIS Report: Wilsonia". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 21 May 2010.
- ^ Rundel, Colin W.; Wunder, Michael B.; Alvarado, Allison H.; Ruegg, Kristen C.; Harrigan, Ryan; Schuh, Andrew; Kelly, Jeffrey F.; Siegel, Rodney B.; Desante, David F.; Smith, Thomas B.; Novembre, John (2013). "Novel statistical methods for integrating genetic and stable isotope data to infer individual-level migratory connectivity". Molecular Ecology. 22 (16): 4163–76. Bibcode:2013MolEc..22.4163R. doi:10.1111/mec.12393. PMID 23906339. S2CID 16556818.
- ^ Graham, Rex (2013). "Ornithologists discover why Wilson's Warbler subspecies vanishing". birdsnews.com.
- ^ a b c d e "All About Birds: Wilson's Warbler Life History". Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology. Retrieved 4 December 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Wilson's Warbler "Wilsonia pusilla"". Boreal Songbird Initiative. 25 February 2014. Retrieved 25 April 2019.
- ^ Semenchuk, Glen Peter (1992). The Atlas of Breeding Birds of Alberta. Nature Alberta. p. 249. ISBN 978-0-9696134-0-4. Retrieved 23 November 2011.
- ^ Curson, Jon; Quinn, David; Beadle, David (1994). New World Warblers. Christopher Helm. pp. 188–189. ISBN 0-7136-3932-6.
- ^ Benedict, Audrey DeLella (2008). The Naturalist's Guide to the Southern Rockies. pp. 431. ISBN 1-55591-535-3
- ^ Gowaty, P.A. (1996). Field studies of parental care in birds: New data focus questions on variation among females. Advance in the Study of Behavior, 25. 477–531.
External links
[edit]- Xeno-canto: audio recordings of Wilson's warbler
- "Wilson's warbler media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Wilson's warbler photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Wilson's warbler Species Account – Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Wilson's warbler - Wilsonia pusilla - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Cardellina
- New World warblers
- Birds of North America
- Native birds of Alaska
- Birds of Canada
- Native birds of the Northwestern United States
- Native birds of the West Coast of the United States
- Birds described in 1811
- Taxa named by Alexander Wilson (ornithologist)
- Birds of Central America

