Camelpox
| Camelpox virus | |
|---|---|
| |
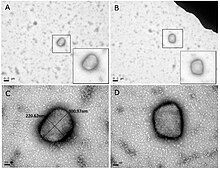
| Transmission electron micrograph of camelpox virus (CMLV) particles | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Varidnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Bamfordvirae |
| Phylum: | Nucleocytoviricota |
| Class: | Pokkesviricetes |
| Order: | Chitovirales |
| Family: | Poxviridae |
| Genus: | Orthopoxvirus |
| Species: | Camelpox virus
|
Camelpox is a disease of camels caused by the camelpox virus (CMPV) of the family Poxviridae, subfamily Chordopoxvirinae, and the genus Orthopoxvirus. It causes skin lesions and a generalized infection. Approximately 25% of young camels that become infected will die from the disease, while infection in older camels is generally more mild.[1] Although rare, the infection may spread to the hands of those that work closely with camels.[2]
Cause
[edit]The camelpox virus that causes camelpox is an orthopoxvirus that is very closely related to the variola virus that causes smallpox. It is a large, brick-shaped, enveloped virus that ranges in size from 265–295 nm. The viral genetic material is contained in a linear double-stranded DNA consisting of 202,182 tightly packed base pairs.[3] The DNA is encased in the viral core. Two lateral bodies are found outside the viral core, and are believed to hold the enzymes required for viral reproduction.[4]
The camelpox virus most often affects members of family Camelidae. However, recent studies show that the disease can be transmitted to both humans and arthropods.[5]
Transmission
[edit]
The camelpox virus is spread in three ways: direct contact, indirect contact, and insect vectors.[citation needed]
In direct contact infection, a camel becomes infected after direct contact with an infected camel.[citation needed]
In indirect contact infection, a camel becomes infected after contact with an infected environment. The virus is spread through milk, saliva, ocular secretions, and nasal secretions, and has been shown to remain virulent outside of a host for four months.[6]
The camelpox virus has been isolated from camel ticks (Hyalomma dromedarii) removed from infected animals. It is believed that the ticks can transmit the disease from camel to camel. This theory is supported by increases in Camelpox infections immediately following heavy rains, during which the camel tick population increases greatly.[7]
Transmission of camelpox to humans was confirmed in 2009 when camel herders in India presented with infections of the hands and fingers. Although other cases of human infection have been reported, no other cases have been verified. Due to the close contact between camels and their human handlers in much of the world, it is believed that camelpox is transmitted to humans via direct contact.[8]
Replication
[edit]The orthopox virus that causes camelpox behaves very similarly to the virus that causes smallpox. After the virus attaches to a host cell, it injects its viral core (the shell containing its DNA) into the cell's cytoplasm. The virus carries DNA polymerase which is used to transcribe its genes. Eventually, the viral core dissolves, and the genetic material is bare within the cytoplasm. When all of the structural proteins have been produced, viral assembly takes place. The newly formed virus particles can be released during cell lysis, or they can derive a host cell produced membrane and be released via budding.[9]
Signs and symptoms
[edit]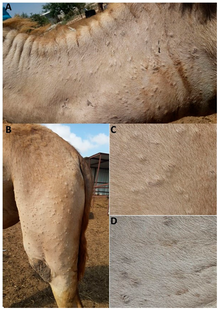
Camels
[edit]The incubation period of camelpox is between 3 and 15 days. The resulting infection can be classified as acute or generalized. Generalized infections are usually found in camels over the age of three, and are characterized by swollen lymph nodes, fever, and the development of skin lesions. The lesions begin as papules, but develop into pustules. These external symptoms usually begin on the head and neck, but eventually spread throughout the body, being especially concentrated on the limbs and genitalia. Without treatment, the animal will generally recover from the infection in 4 to 6 weeks.[6]
Acute infections are usually found in camels under the age of three, and result in mild to severe systemic infections. In addition to the symptoms that accompany a generalized infection, these animals experience internal lesions along the lining of the mouth, and respiratory and digestive tracts. They also experience loss of appetite and diarrhea. A large proportion of camels acutely infected with camelpox die, although death is often attributed to a secondary infection.[10]
Humans
[edit]Camelpox infections in humans result in mild skin lesions on the hands and fingers. Reports have been made that the lesions can be found on the mouth and lips if the patient drank milk from an infected camel, but these symptoms have not been confirmed.[8]
Diagnosis and treatment
[edit]Camelpox diagnosis can be based on symptoms. However, both Camel Contagious Ecthyma and Camel Papillomatosis cause indistinguishable symptoms under similar conditions.[11] Therefore, the best way to diagnose Camelpox is via Transmission Electron Microscopy evaluation of skin samples from infected animals. The camelpox virus has a unique shape that is readily identifiable using this method. In cases where TEM technology is not available, serological tests are available to identify camelpox as the causative agent for infection.[6] Additionally, researchers in India are working on a diagnostic polymerase chain reaction to quickly and effectively identify the camelpox virus.[12]
When the camelpox virus is identified as the causative agent, the disease can be treated with anti-viral medications. The most common medication used to treat camelpox is Cidofovir, a broad spectrum anti-viral that acts by inhibiting the viral DNA polymerase. Cidofovir has proven to be 100% effective at preventing death in infected camels.[13]
Prevention
[edit]Camelpox outbreaks have a negative effect on the local economies. Outbreaks often lead to the loss of young camels, and render older camels useless in terms of milk and meat production, and transportation. As such, attempts are often made to prevent transmission of the disease. An attenuated vaccine is currently available that provides long term protection against camelpox if administered when the camel is at least 9 months old. An inactivated vaccine is also available, but must be administered yearly to maintain protection.[6]
The camelpox virus is sensitive to a number of common disinfectants. It can also be destroyed by autoclaving, short term exposure to UV light, and boiling for at least 10 minutes. These methods may be used by camel herders to minimize risk of environmental contamination.[6]
Society and culture
[edit]In 1995 Saddam Hussein admitted to having a number of top Iraqi scientists working to turn camelpox into a biological weapon. Camelpox was chosen for two main reasons: the theory that the local population would be largely immune, and its relation to smallpox. It is believed that the reported cases of camelpox infection in humans is low due to an immunity gained from exposure to camels during early childhood. Therefore, a significant proportion of Iraq's population would be immune to camelpox, while troops from non-camel herding countries would be susceptible.[14] It is not believed that the research process was successful, or that the virus was ever produced in any great quantities.[15]
Notes and references
[edit]- ^ Fenner, Frank J.; Gibbs, E. Paul J.; Murphy, Frederick A.; Rott, Rudolph; Studdert, Michael J.; White, David O. (1993). Veterinary Virology (2nd ed.). Academic Press, Inc. ISBN 978-0-12-253056-2.
- ^ Carter, G.R.; Wise, D.J. (2006). "Poxviridae". A Concise Review of Veterinary Virology. Archived from the original on 26 June 2005. Retrieved 10 June 2006.
- ^ Gubser, Caroline; Smith, Geoffrey (2001). "The sequence of Camelpox virus shows it is most closely related to Variola virus, the cause of smallpox". Journal of General Virology. 83 (4): 855–872. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-83-4-855. PMID 11907336.
- ^ "Poxviruses". Archived from the original on 15 October 2018. Retrieved 2 April 2012.
- ^ Jezek, Z; Kriz, B (1983). "Camelpox and its risk to the human population". Journal of Hygiene, Epidemiology, Microbiology, and Immunology. 27 (1): 29–42. PMID 6304186.
- ^ a b c d e "Camelpox" (PDF). Terrestrial Animal Health Code. World Organization for Animal Health. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 June 2012. Retrieved 31 March 2012.
- ^ Wernery, U; Kaaden (1997). "Orthopox virus infections in dromedary camels in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) during winter season". Journal of Camel Practice and Research. 4 (1): 51–55.
- ^ a b Bera, BC (August 2011). "Zoonotic cases of camelpox infection in India". Journal of Veterinary Microbiology. 152 (1–2): 29–38. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.04.010. PMID 21571451.
- ^ "Orthopoxvirus". Virus Zone.
- ^ Pfeffer, M (January 1998). "Fatal Form of Camelpox Virus Infection". The Veterinary Journal. 155 (1): 107–109. doi:10.1016/s1090-0233(98)80045-2. PMID 9455166.
- ^ Khalafalla, A (1998). "Epizootiology of Camel Pox, Camel Contagious Ecthyma and Camel Papillomatosis in the Sudan". Animal Production Under Arid Conditions. 2: 115–131.
- ^ Balamurugan, Vinayagamurthy (March 2009). "A Polymerase Chain Reaction Strategy for the Diagnosis of Camelpox". Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 21 (2): 231–237. doi:10.1177/104063870902100209. PMID 19286503.
- ^ Andrei, Graciela; Robert Snoeck (December 2010). "Cidofovir Activity against Poxvirus Infections". Viruses. 2 (12): 2803–2830. doi:10.3390/v2122803. PMC 3185586. PMID 21994641.
- ^ Coghlan, Andy (17 April 2002). "Fear Over Camelpox as Bioweapon". NewScientist. Archived from the original on 25 August 2014. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ^ Pike, John. "Iraq Special Weapons". Federation of American Scientists. Archived from the original on 25 October 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
