Comrat
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2016) |
Comrat
Komrat | |
|---|---|
| |
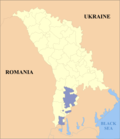
Location of Comrat in Moldova | |
| Coordinates: 46°19′N 28°40′E / 46.317°N 28.667°E | |
| Country | |
| Autonomous Region | |
| Founded | 1443/1789 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Sergey Anastasov[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 164 km2 (63 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Total | 20,113 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (320/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Climate | Cfb |
| Website | http://comrat.md |
Comrat (Romanian: Comrat, Romanian pronunciation: [komˈrat]; Gagauz: Komrat, Russian: Комрат) is a city and municipality[3] in Moldova and the capital of the autonomous region of Gagauzia. It is located in the south of the country, on the Ialpug River. In 2014, Comrat's population was 20,113, of which the vast majority are Gagauzians.[2]
History
[edit]
Comrat was first settled as early as 1443, with other sources claiming it was founded in 1789. Nevertheless, the settlement was sparsely populated until the new Russian government issued a decree in 1819 to resettle the region with Bulgarians and other nationalities from across the Danube,[4] after the territory was annexed by Russia from Moldavia in 1812.
In 1906, the village revolted against the Russian authorities and proclaimed the autonomous (but not independent) Comrat Republic.[5][6] Following World War I, it was part of Kingdom of Romania. During World War II, it was occupied by the Soviet Union in 1940, before it was recaptured by Romania in 1941.
During the time when the town was part of Moldavian SSR, Comrat's industry was geared toward the production of butter, wine, and rugs, the latter decorated with Moldavian motifs. The Comrat State University was established in 2002.
Demographics
[edit]According to the 2014 census, the population of Comrat amounted to 20,113 inhabitants (making it the tenth largest city in Moldova), a decrease compared to the previous census in 2004, when 23,327 inhabitants were registered. Of these, 9,528 were men and 10,585 were women.[7]
Ethnic composition of Comrat (2014)[8]
Footnotes:
* There is an ongoing controversy regarding the ethnic identification of Moldovans and Romanians.
* Moldovan language is one of the two local names for the Romanian language in Moldova. In 2013, the Constitutional Court of Moldova interpreted that Article 13 of the constitution is superseded by the Declaration of Independence,[10] thus giving official status to the name Romanian.[11][12]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1930 | 12,331 | — |
| 1959 | 14,361 | +16.5% |
| 1970 | 21,369 | +48.8% |
| 1979 | 23,652 | +10.7% |
| 1989 | 25,822 | +9.2% |
| 2004 | 23,327 | −9.7% |
| 2014 | 20,113 | −13.8% |
Economy
[edit]Comrat is situated in the southern wine zone of Moldova. It is known for production of red wine and muscat. In Comrat and its suburbs there are about 10 wineries.
Food production is very developed in the city. Comrat is a home for food processing factories, alcohol production, and an oil processing plant (the first and only one in Moldova).
There is also such economic agents as a ferro-concrete factory, furniture productions, wood processing, production of plastic windows and doors, cattle butcheries, and transport companies.
Sport
[edit]Football clubs FC Olimp Comrat and Univer-Oguzsport are based in Comrat.
Geography
[edit]Climate
[edit]Comrat has a humid continental climate (Dfa), characterized by warm summers and cool, drier winters with snow. Winter lows are often below 0 °C (32 °F). In summer, the average maximum temperature is approximately 25 °C (77 °F). The average annual precipitation is relatively low.
| Climate data for Comrat (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
4.1 (39.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
17.0 (62.6) |
23.0 (73.4) |
26.9 (80.4) |
29.3 (84.7) |
29.1 (84.4) |
23.2 (73.8) |
16.2 (61.2) |
9.0 (48.2) |
3.1 (37.6) |
16.0 (60.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
0.1 (32.2) |
4.8 (40.6) |
11.0 (51.8) |
16.8 (62.2) |
20.9 (69.6) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
17.3 (63.1) |
11.1 (52.0) |
5.2 (41.4) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
10.9 (51.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −4.5 (23.9) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
0.7 (33.3) |
5.9 (42.6) |
11.2 (52.2) |
15.4 (59.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
17.1 (62.8) |
12.2 (54.0) |
7.0 (44.6) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
6.6 (43.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 33 (1.3) |
27 (1.1) |
32 (1.3) |
37 (1.5) |
48 (1.9) |
69 (2.7) |
59 (2.3) |
46 (1.8) |
42 (1.7) |
43 (1.7) |
39 (1.5) |
39 (1.5) |
514 (20.2) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 71 |
| Source: NOAA[13] | |||||||||||||
Notable people
[edit]- Petar Draganov (1857 in Komrat - 1928) Russian philologist and Slavist
- Reuven Shari (1903 in Comrat – 1989) was a Russian-born Israeli politician
- Alexandru Bârlădeanu (1911 in Comrat – 1997) a Romanian Marxian economist who was prominent during the Communist regime, sidelined in 1968
- Sorana Gurian (1913 in Comrat – 1956) a writer, journalist, and translator, emigrated to Israel and France
- Anatoliy Blashku (born 1944 in Komrat) was the Minister of Industry of Transnistria, a Moldovan who moved to Tiraspol as a teenager
- Alexandr Stoianoglo (born 1967 in Comrat) a Moldovan politician and member of the Parliament of Moldova since 2009.
- Irina Vlah (born 1974 in Comrat) a Moldovan politician, Governor (Başkan) of the Autonomous Territorial Unit of Gagauzia
- Igor Cobileanski (born 1974 in Comrat) a Moldovan film director
- Mihai Cojusea (born 1978 in Comrat) a Moldavian football striker who plays for CF Gagauziya
- Alexander Romanov (born 1990 in Comrat) a Moldavian UFC heavyweight fighter
International relations
[edit]Twin towns — Sister cities
[edit]Comrat is twinned with:
Gallery
[edit]-
Central Square
-
Central Park
-
Hotel "Altyn Palace"
-
Shopping center "Comrat-City"
-
Lenin statue
-
Street in Comrat
References
[edit]- ^ Açik TV. "Viktor Volkov will perform the duties of the mayor of Comrat Archived 2016-01-03 at the Wayback Machine"
- ^ a b Results of Population and Housing Census in the Republic of Moldova in 2014: "Characteristics - Population (population by communes, religion, citizenship)" (XLS). National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova. 2017. Retrieved 2017-05-01.
- ^ LEGE Nr. 248 din 03.11.2016 pentru modificarea și completarea Legii nr. 764-XV din 27 decembrie 2001 privind organizarea administrativ-teritorială a Republicii Moldova (in Romanian)
- ^ http://aboutmoldova.md/ro/view_free.php?id=365 (in Romanian)
- ^ "107 лет назад в Буджаке была провозглашена Комратская республика". vfokuse.md (in Russian). 9 January 2013. Archived from the original on 20 August 2017.
- ^ "106 лет назад была провозглашена Комратская республика". Gagauzinfo.MD (in Russian). 9 January 2012.
- ^ "2014 Moldova Census of Population and Housing". National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova. (in Romanian, Russian, and English)
- ^ "2014 Moldova Census of Population and Housing". National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova. (in Romanian, Russian, and English)
- ^ "2014 Moldova Census of Population and Housing". National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova. (in Romanian, Russian, and English)
- ^ "Hotărâre Nr. 36 din 05.12.2013 privind interpretarea articolului 13 alin. (1) din Constituție în corelație cu Preambulul Constituției și Declarația de Independență a Republicii Moldova (Sesizările nr. 8b/2013 și 41b/2013)" (in Romanian). Constitutional Court of Moldova. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
124. ... Prin urmare, Curtea consideră că prevederea conținută în Declarația de Independență referitoare la limba română ca limbă de stat a Republicii Moldova prevalează asupra prevederii referitoare la limba moldovenească conținute în articolul 13 al Constituției.
[124. ... Therefore, the Court considers that the provision contained in the Declaration of Independence regarding the Romanian language as the state language of the Republic of Moldova prevails over the provision regarding the Moldovan language contained in Article 13 of the Constitution.] - ^ "Moldovan court rules official language is 'Romanian', replacing Soviet-flavored 'Moldovan'". Fox News. Associated Press. 2013-12-05. Archived from the original on 2013-12-09. Retrieved 2013-12-07.
- ^ "Chisinau Recognizes Romanian As Official Language". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 5 December 2013. Archived from the original on 23 September 2016. Retrieved 11 March 2014.
- ^ "Comrat Climate Normals 1991–2020". World Meteorological Organization Climatological Standard Normals (1991–2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 21 August 2023. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- ^ "Примэрия мун. Комрат".